Hydrogen peroxide’s discovery was done by a French chemist J.L.Thenard. We write molecular formula of hydrogen peroxide as .
Preparation of Hydrogen peroxide: Hydrogen peroxide can be prepared in the laboratory by the action of cold, dilute sulphuric acid on sodium or barium peroxide. Let’s have a look at each of them one by one:
- From sodium peroxide ( Merck’s process):
It is prepared by adding a calculated amount of sodium peroxide into cold, dilute solution of sulphuric acid. This addition is carried out slowly in a small amount with constant stirring. Na2O2+H2SO4→Na2SO4+H2O2
Upon cooling, we get crystal of Na2SO4.10H2O. The crystals of Na2SO4.10H2O are decanted leaving behind the solution of hydrogen peroxide. By this method, 30 - From barium peroxide: J.L.Thenard first prepared hydrogen peroxide in 1818 by acidifying barium peroxide and removing the excess of water by evaporation under reduced pressure. By this method, a paste of hydrogen peroxide is obtained in ice-cold water and is treated with a cold solution of sulphuric acid.
BaO2.8H2O(s)+H2SO4(aq)→BaSO4(s)+H2O2(aq)+8H2O(l)
The white ppt. of barium sulphate is removed by filtration leaving behind 5% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
Structure of Hydrogen peroxide:
Hydrogen peroxide has a non-planar structure in which two hydrogen atoms are arranged in two directions almost perpendicular to each other and to the axis joining the two oxygen atoms.
The O-O linkage is called the peroxide linkage. The structure of H2O2 in the solid and gas phase are shown below:
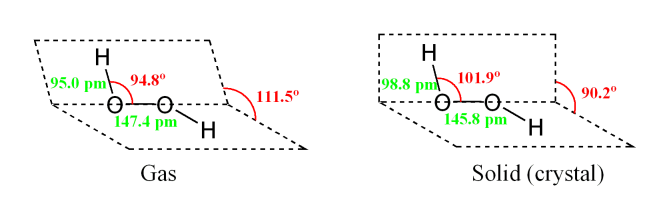
Chemical reactions of Hydrogen peroxide:
Decomposition reaction:
Pure Hydrogen peroxide is an unstable liquid, hence decomposes into water and oxygen upon heating.
2H2O2(l)→2H2O(l)+O2(g)
In hydrogen peroxide oxidation state of oxygen is -1 which is intermediate between the values for O2 (zero) and H2O (-2). Therefore, an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide readily decomposes.
Reactions as an oxidizing agent:
- In acidic medium: In presence of an acid, H2O2 can accept electrons and act as an oxidizing agent. See the reaction here: H2O2+2H++2e−→2H2O
- In alkaline medium: Hydrogen peroxide can also accept electrons in the alkaline medium and act as an oxidizing agent. H2O2+OH−+2e−→3OH−
Reactions as a reducing agent:
- In acidic medium: Hydrogen peroxide has a tendency to take up oxygen from strong oxidizing agents and thus, act as a reducing agent.H2O2→2H++O2+2e−
- In alkaline medium: H2O2+2OH−→2H2O+O2+2e−
Bleaching action:
Hydrogen peroxide acts as a bleaching agent due to the release of nascent oxygen. It oxidizes the coloring matter to a colorless product. It is used to bleach materials like silk, wool, ivory, feathers, etc.
Addition reactions:
Hydrogen peroxide on adding with alkenes form glycols.
Uses of Hydrogen Peroxide:
- Hydrogen peroxide is domestically used as hair bleach and as a mild disinfectant.
- It is used as a bleaching agent in industries like textiles, papers, straw, leather, fats, etc.
- Hydrogen peroxide is also used as an antiseptic for washing wounds, ears and teeth under the chemical name perhydrol.
- It is used for the production of propylene oxide, epoxides and polyurethanes.
- It is used in the manufacture of many inorganic compounds such as percarbonates, sodium perborates which are important constituents of high-quality detergents.