Potassium is required for the function of all living cells, thus it is present in all plant and animal tissues. It is an essential micronutrient and main intracellular ion of all the cells. Potassium also maintains the fluid and electrolyte balance of body fluids. Potassium is mainly found in high concentrations in plants. The high concentration of potassium in the plant is related to a low concentration of sodium. Potassium was first isolated from the plant which means potash and as it has given name potassium.
The Dietary measure of potassium:
- The adequate intake of potassium for men and women of the age of 14 is 4700 mg. adequate intake for pregnant women is 4700 mg/day and for the lactation period it is 5100 mg/day.
- For infants it is 400 mg, from 6-12 months Ai is 700 mg and from 1-13 years adequate intake is about 3000 to 4500 mg/day.
Importance of potassium in plants:
- The high concentration of potassium in plants suggests that heavy crop production rapidly depletes the soils containing potassium.
- The agricultural fertilizers consume 93
Potassium deficiency in plants:
- Potassium deficiency in plants is also known as potash deficiency. This disorder is most common on sandy, light soils because potassium ions are highly soluble and they get leached easily from soils without colloids.
- Potassium deficiency in the plant causes brown scorching and curling of leaf tips and also causes chlorosis between the leaf veins.
- Potassium deficiency reduces plant growth, root development, and seed and fruit development.
Importance of potassium in animals:
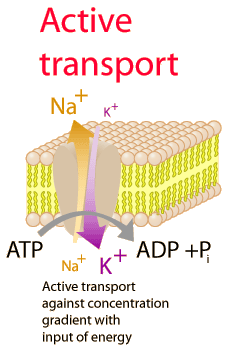
- Potassium is the major cation inside animal cells, whereas the sodium is present majorly outside the cells. This difference between these two charge particle produces electric potential between inside and outside of cells, known as the membrane potential.
- The membrane potential created by these two ions results in the production of an action potential. This ability of producing action potential by the cells is important for body functions such as neurotransmission, heart function, and muscle contraction.
Potassium deficiency in animals:
High blood pressure (hypertension) :
Low potassium level increases the risk of hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and stroke.
Hypokalemia :
A severe shortage of potassium in body fluids can lead to a fatal condition known as hypokalemia. It generally results from loss of potassium through dieresis, diarrhea, or vomiting. The symptoms of hypokalemia include muscle weakness and cramps, ECG abnormalities, decreased reflex response and respiratory paralysis in severe cases.
Side effects of potassium supplements:
- The most common side effects of potassium supplements are gastrointestinal symptoms. These include vomiting, nausea, abdominal discomfort, or diarrhea. To reduce these side effects potassium supplements should be taken with meals.
- Hyperkalemia is also one of the critical side effects of potassium. When potassium builds up faster than the kidneys can excrete it results in hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia is common in individuals having renal failure. The symptoms of hyperkalemia include muscular weakness, tingling of hands and feet, and temporary paralysis.
Food sources of potassium:
- Foods with a high concentration of potassium include potatoes, orange juice, kiwi, avocados, bananas, turnip, coconut, apricots, etc.
- The most concentrated food with potassium includes sun-dried tomatoes, dried herbs, whey powder, chocolate, rice bran, molasses, etc.