Family Fabaceae (Leguminosae)
It is the 3rd largest family in flowering plants. It was earlier called Papilionidae, a subfamily of family Leguminosae. They are distributed all over the world.
Vegetative characters

| Habitat | – | Usually herbs or herbaceous climbers. |
| Leaves | – | Alternate, pinnately compound, or simple.usually stipulate leaves with pulvinous base. Reticulate Venation. |
| Root | – | The lateral roots have nodules containing nitrogen fixing bacteria. |

Floral characters
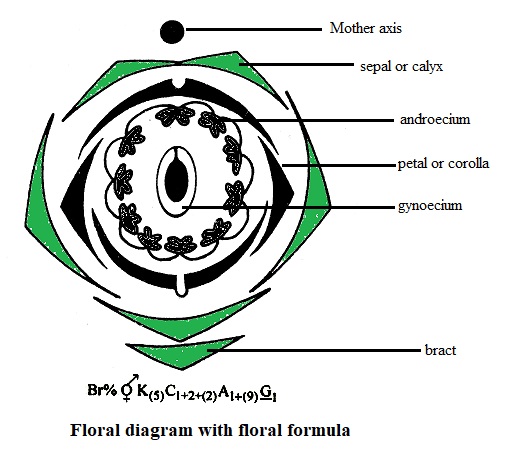
| Inflorescence | – | Axilliary or terminal, Racemose inflorescence. |
| Flower | – | Bracteate, bracteolate, Complete, Bisexual, Zygomrphic. |
| Calyx | – | Sepals 5, Gamosepalous; Valvate/Imbricate Aestivation. |
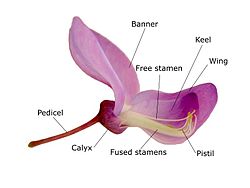
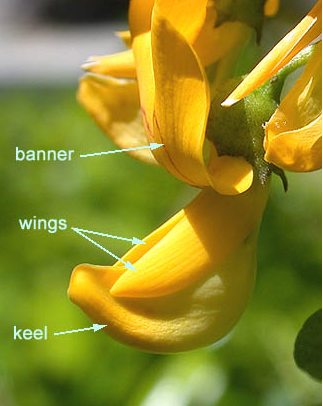
| Corolla | – | Petals 5, Polypetalous, Papilionaceous, Petals unequal, consisting of a posterior standard (Vexillium), two lateral wings (Alae), two anterior ones forming a keel or Carina (enclosing stamens and pistil), vexillary aestivation |
| Androecium | – | Stamens 10, Diadelphous, Anther dithecous |
| Gynoecium | – | Ovary superior, Mono-carpellary, Unilocular with many ovules, Marginal placentation, Style single. |
| Fruit | – | Legume; Seed: 1 To Many, Non-endospermic. |
Floral Formula:
Br
Floral Diagram Economic importance Many plants belonging to the family are sources of