Complex tissue is composed of more than one type of cells (heterogeneous cells) working together as a single unit. In plants, xylem and phloem are the complex tissues, and they are the major components of the vascular bundles. Complex tissue is found in almost every part of the plant body as it is involved in the conduct of water and food materials throughout the body.
Xylem (Wood)
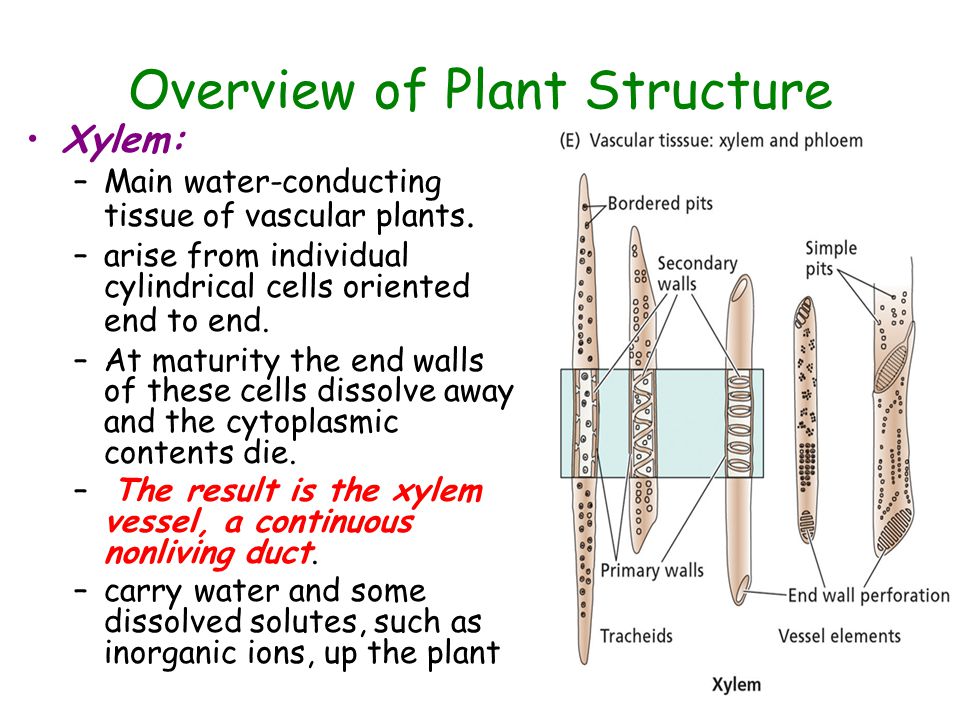
Xylem tissue forms a long channel (from the tip of the root to all parts of the plant) for the conduction of water and minerals throughout the plant body. It also provides mechanical support for the plant.
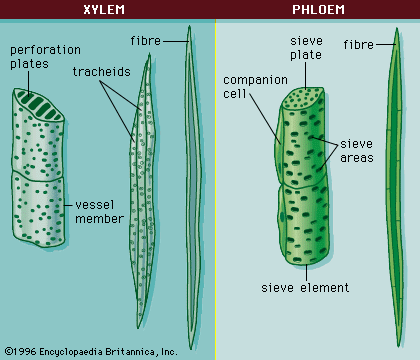
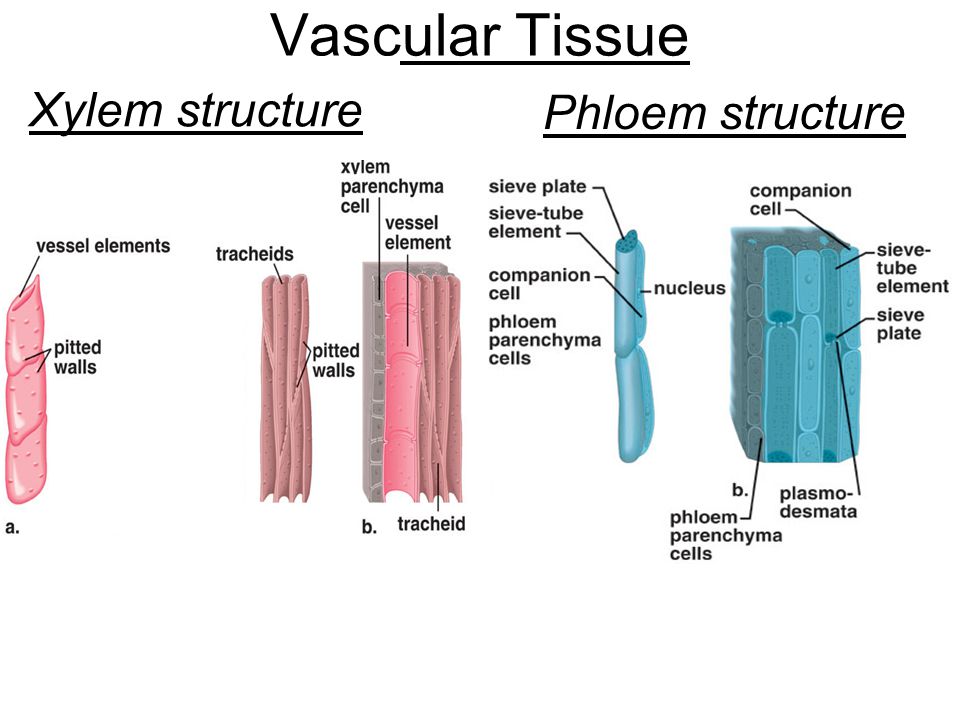
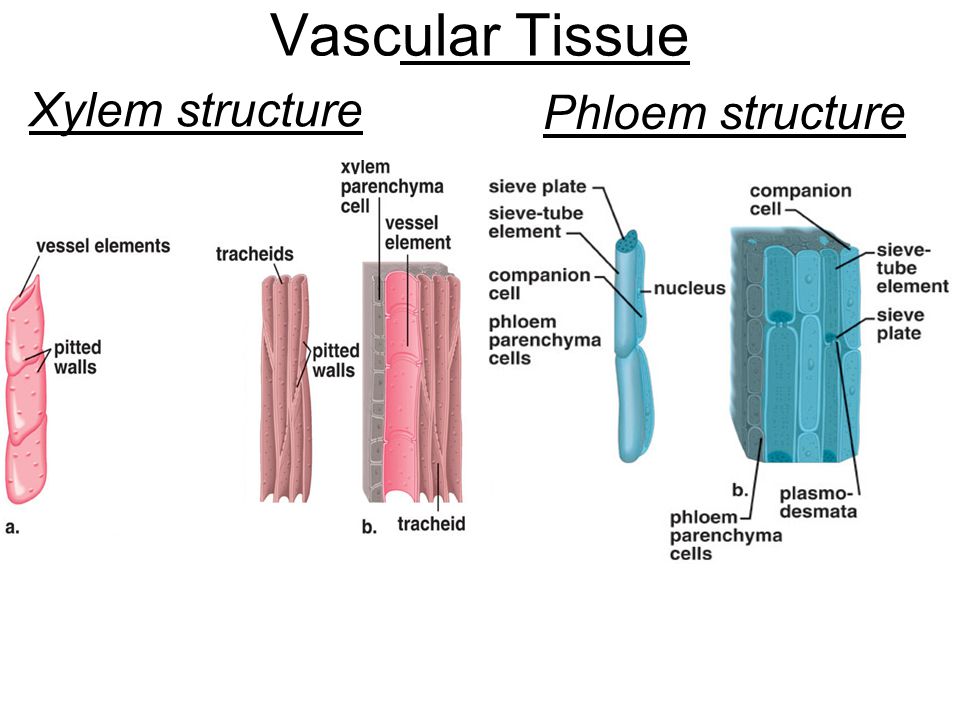
It is composed of four types of cells: xylem tracheids, xylem vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma. Xylem tracheids and vessels are together known as tracheary elements.
Xylem Tracheids
- Tracheids are elongated tube like cells with pointed or tapering ends.
- The cell wall is hard and lignified. The cells have a large cell cavity.
- They are empty dead cells and the cell walls are provided with one or more rows of pits (bordered).
- The diffusion of water and salts takes place through these pits.
- They do not have any perforation plates at their cross walls.
Xylem Vessels
- Xylem vessels are also known as tracheae, and are composed of dead cells.
- They are cylindrical and tubular structures.
- Vessels are formed of a row of cells placed end-by-end followed by dissolution of cell walls at the point of meet.
- The end walls of xylem vessels possess perforation plates, which helps in connecting the xylem members to each other.
- The cell walls are thickened in various ways. Based on these thickenings, xylem vessels are named as annular, spiral, scalariform, reticulated and pitted vessels.
Xylem Fibres
- Xylem fibres are dead cells. These are the sclerenchyma fibres found in association with xylem elements to provide mechanical strength.
- The cell walls are thickened and highly lignified.
- The cells lack protoplast, and the pits on the walls are simple without any borders.
Xylem Parenchyma
- It is the only living component in the xylem tissue.
- These cells are involved in short distance transport of materials.
- They are also involved in storage of sugars, starch and lipids.
Classification of Xylem tissue
On the basis of structure and time of origin, it is classified into 2 types.
- Protoxylem: It is the first formed xylem, and is composed of small tracheids and vessels.
- Metaxylem: It is the later formed xylem and consists of larger tracheids and vessels.
![image_thumb[16].png](https://www.w3schools.blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/image_thumb16-png.png)
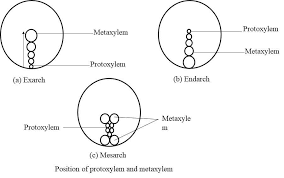
On the basis of the position of protoxylem, it is also classified into 3 types.
- Exarch: Protoxylem faces towards the cortex. (e.g. Roots)
- Endarch: Protoxylem faces towards the pith. (e.g. Stems)
- Mesarch: Protoxylem is present between the metaxylems. (e.g. Ferns)