C# Function
A block of code with a signature that is used to execute the specified statements is called a function in C#.
Components of a Function:
- Function name: It is used to specify a unique name to be used for calling a Function.
- Return type: It is used to define the data type of the return value of the function.
- Body: It is used to define a block for executable statements.
- Access specifier: It is used to define the accessibility of the function in an application.
- Parameters: It is used to specify a list of parameters to be passed during the function call.
Syntax:
<access-specifier><return-type>FunctionName(<parameters>) { // function body // return statement } |
Explanation:
It is optional to specify the Access-specifier, parameters and return statement.
C# Function: using no parameter and return type.
Example:
using System; namespace Func_xample { class Example { public void Display() { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!!"); } static void Main(string[] args) { Example xyz = new Example(); xyz.Display(); } } } |
Output:
![]()
Explanation:
In the above example, we are creating a function without any parameters, also known as the non-parameterized function and also without any return type. The return type is thus void.
C# Function: using parameter but no return type.
Example:
using System; namespace FuncExample { class Example { public void Display(string msg) { Console.WriteLine("Hello " + msg); } static void Main(string[] args) { Example xyz = new Example(); xyz.Display("World!!"); } } } |
Output:
![]()
Explanation:
In the above example, we are creating a function with the parameters but no return types.
C# Function: using parameter and return type.
Example:
using System; namespace FuncExample { class Example { public string Display(string msg) { Console.WriteLine("Message for you!!"); return msg; } static void Main(string[] args) { Example xyz = new Example(); string msg = xyz.Display("World!!"); Console.WriteLine("Hello "+ msg); } } } |
Output:
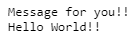
Explanation:
In the above example, we are creating a function with both the parameters and return types.