C# finally
Whether the exception is handled or not, we need to execute the important code. To serve this purpose in C#, the finally block is used after the catch or try block.
Example: When the exception is handled:
using System; public class Example { public static void Main(string[] args) { try { int X = 300; int Y = 0; int Z = X/Y; } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } finally { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!!"); } Console.WriteLine("Today is a Great day!!"); } } |
Output:
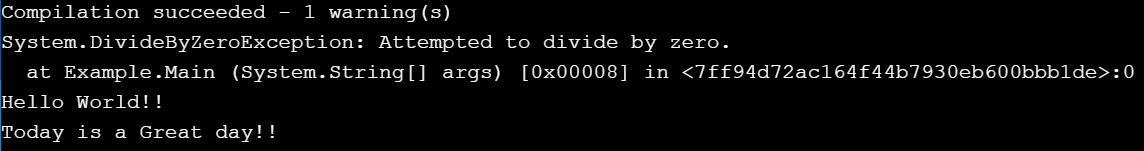
Explanation:
In the above example, we are displaying the use and behavior of the C# finally block when the exception is handled.
Example: When an exception is not handled:
using System; public class Example { public static void Main(string[] args) { try { int X = 300; int Y = 0; int Z = X/Y; } catch (NullReferenceException e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } finally { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!!"); } Console.WriteLine("Today is a Great day!!"); } } |
Output:
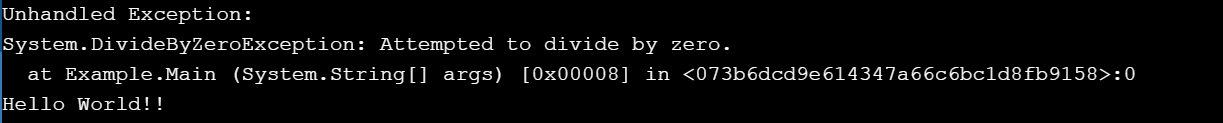
Explanation:
In the above example, we are displaying the use and behavior of the C# finally block when the exception is not handled.