Sexual dimorphism
-
- They show sexual dimorphism.
- Male frogs produce sound sounds during mating.
- Hence, they possess sound producing vocal sacs.
- They also have a copulatory pad (nuptial pad) on the first digit of the fore limbs.
- Both these are absent in female frogs.

Male reproductive organ
- The male reproductive system is composed of a pair of testes, a long duct called vas effertia, urinogenital duct and a cloacal opening.
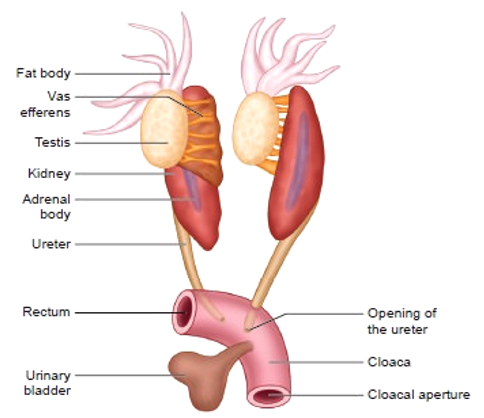
- Testis
- The testis is yellow in color and ovoid in shape.
- Each testis is found attached to the upper part of the kidney by a doubly folded peritoneum known as mesorchium
- Vas efferentia
- A group (10 – 12 in number) of ducts called vas efferentia arises from the testis.
- They enter into the kidneys, and then open into Bidder’s canal.
- The duct then continues to join the urinogenital duct that comes out of the kidneys and opens into the cloaca.
- The cloaca is a small, common chamber that is used to pass faecal matter, urine and sperms to the exterior.
Female reproductive organ
The female reproductive consists of a pair of ovaries, oviducts, ostia, ovisacs and a cloacal opening.
Ovary
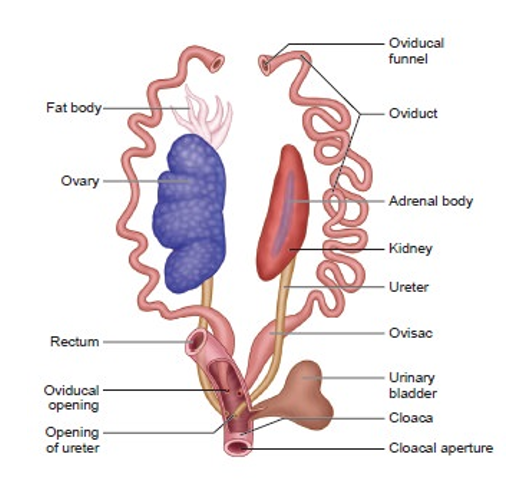
- A pair of ovaries is present near the kidneys.
- They are attached to the kidneys by means of folds of peritoneum called mesovarium.
- But they do not have any functional connection with kidneys.
Oviduct
- A pair of coiled oviducts arising from the ovaries lies on the side of the kidneys.
- Each oviduct opens into the body cavity through a funnel-shaped opening called ostia.
Ovisac
- At the posterior end, oviduct dilates to form ovisacs.
- The ovisacs store eggs temporarily before they are released through cloaca.
Fertilization & Development
Fertilization is external and takes place in water. Both eggs and sperms are released to the water during spawning.
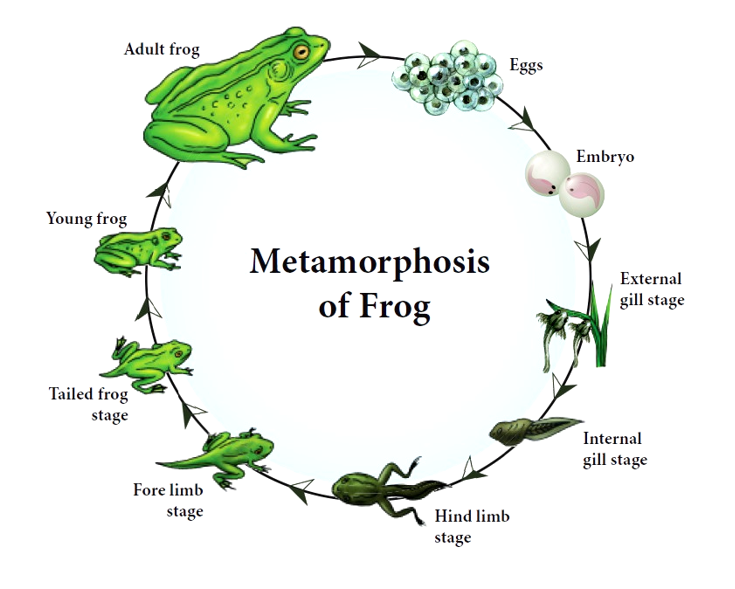
Development involves a larval stage called tadpole. They are hatched from eggs within a few days after fertilization.
Tadpole undergoes metamorphosis to form the adult.
- For a newly hatched tadpole, the first source of food is the yolk stored in its body.
- They gradually grow larger and develop three pairs of gills.
- After metamorphosis, the tadpoles get transformed into an air – breathing carnivorous adult frog
- Legs grow from the body, and the tail and gills disappear.
- The mouth broadens, developing teeth and jaws, and the lungs become functional.