Addison’s disease is an uncommon disorder occurring when the body does not produce enough of certain hormones, hence the term adrenal insufficiency. This disorder makes the adrenal glands to produce insufficient cortisol and too little aldosterone. It occurs across all ages and can be fatal if not treated.
Symptoms.
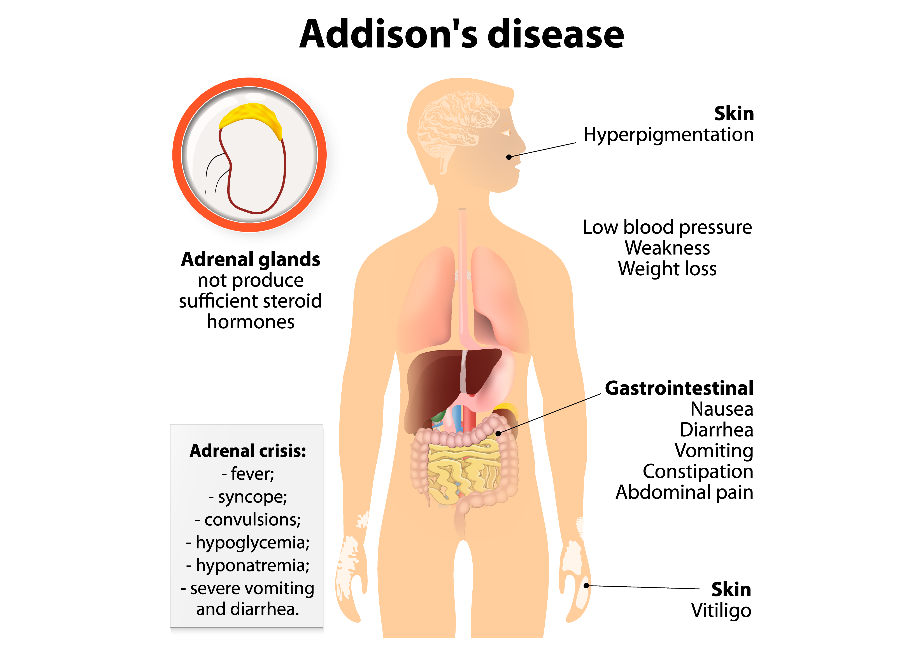
- Tiredness and fatigue.
- The weakness of the muscles.
- Skin color darkening.
- Low blood sugar levels.
- Mouth sores.
- Fainting spells.
- Decreased appetite and weight loss.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Salt cravings.
Addison’s disease may also cause neuropsychiatric symptoms such as:
- Depression and irritability.
- Disturbances in sleep.
- Lack of energy.
The disease can lead to Addison’s crisis if left untreated for long, where the signs and symptoms include:
- Delirium.
- Agitation.
- Auditory and visual hallucinations.
- High fever.
- Unconsciousness.
- Mental status changes, e.g., fear, restlessness, and confusion.
Addison’s crisis is a life-threatening medical emergency and if left untreated can lead to shock and death. Addison’s disease is classified into two major groups;
- Primary adrenal insufficiency.
- Secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Primary adrenal insufficiency.
Occurs in a situation where there is severe damage of the adrenal glands to the point that they can no longer produce hormones. It is caused by an autoimmune disease, where the immune system attacks the adrenal glands. The immune system mistakes any given area or organ of the body for a bacteria or virus thus attacking it. Other causes of primary adrenal insufficiency are:
- Cancer and tumors.
- Body infections.
- Prolonged use of glucocorticoids such as prednisone.
- Some blood thinners for the control of clotting in the blood.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency happens when the pituitary glands (found in the brain), are unable to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), whose function is to tell the adrenal glands when to secrete hormones.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency may also occur in cases where an individual does not take the corticosteroid medications prescribed by the doctor, used to help in the control of chronic health conditions such as asthma.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency may also be caused by:
- Tumors.
- Genetics.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Medications.
People at higher risks of Addison’s disease.
Individuals maybe at higher risks of suffering from Addison’s disease if they:
- Suffer from cancer.
- Suffer chronic diseases such as tuberculosis.
- Undergo surgery to remove a given part of adrenal glands.
- Take blood thinners/anticoagulants.
- Suffer from an autoimmune disease such as Graves’ disease or type I diabetes.
Diagnosis of Addison’s disease.
The doctors ask for the medical history and the symptoms experienced by the patient. A physical examination is conducted and order some lab tests to check potassium and sodium levels in the patient’s body. Doctors may also do image tests and measure hormone levels.