Forms in Angular 8 are used to handle the user’s input, enable users to log in, update profile, enter information, and to perform different data-entry tasks. To handle the user’s input through forms, there are 2 approaches in Angular 8:
- Reactive forms
- Template-driven forms
Reactive Forms vs. Template-driven Forms:
For the collection of the user’s input events from the view, validation of the user’s input, creation of a form model and data model to update, and to facilitate a way to track changes, the Reactive forms, and Template-driven forms are used. However, each of these approaches manages and processes the data differently, offering different advantages.
Reactive Forms:
- More robust.
- More scalable, reusable, and testable.
- Best to use if forms are a key part of your application, or the application is already built using reactive patterns.
Template-driven Forms:
- Best to use to add a simple form to an application, such as email list signup form.
- Easy to use in the application.
- Not as scalable as Reactive forms.
- Most preferred to use if an application requires a very basic form and logic.
- Easily managed in a template.
Example: Angular reactive form:
- Create an Angular form app and name it as ang8form.
- Run the server. Use the below commands.
- ng new ang8form
- cd ang8form
- ng serve
- Install Bootstrap 4.
Command: npm install bootstrap –save
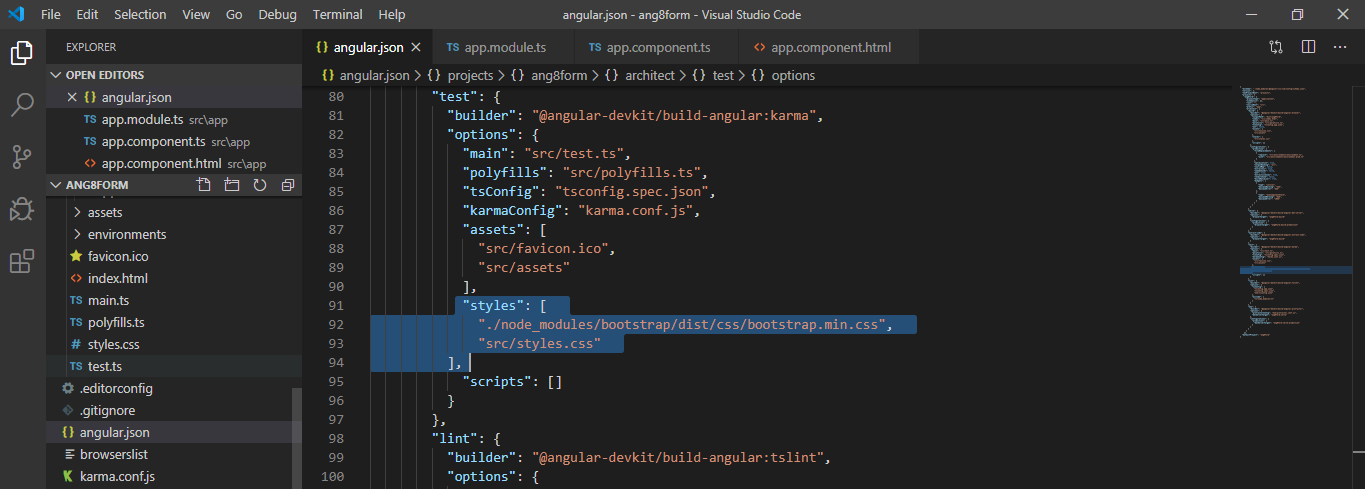
- The bootstrap 4 is now required to be included inside the angular.json file inside the styles array.
"styles": [ "./node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css", "src/styles.css" ], |
- Register the Reactive Forms Module
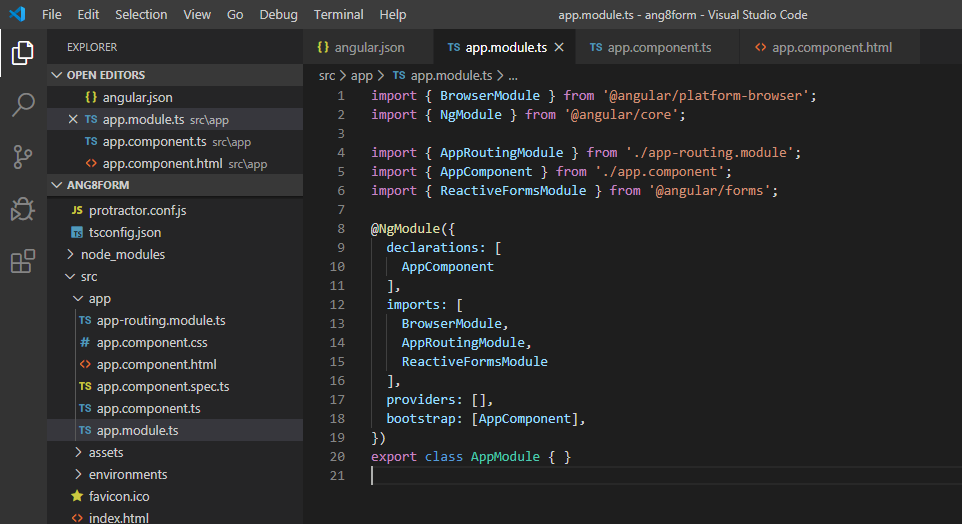
Import the ReactiveFormsModule from the @angular/forms package. To use the reactive forms, the imported module is added to the app.module.ts file’s import array.
app.module.ts:
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule, AppRoutingModule, ReactiveFormsModule ], providers: [], bootstrap: [AppComponent], }) export class AppModule { } |
- Add FormControl class.
- Register the control into the template.
- Update the FormControl value.
The FormControl class which is the basic building block used in reactive forms is imported into the component to register a single form-control. A new instance of the form control is created to save as a class property.
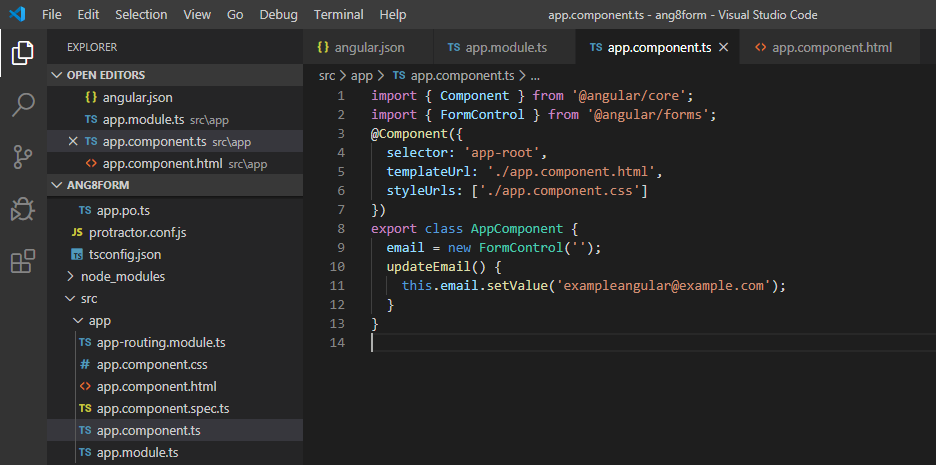
- Modify the app.component.ts file.
app.component.ts:
import { Component } from '@angular/core'; import { FormControl } from '@angular/forms'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'] }) export class AppComponent { email = new FormControl(''); updateEmail() { this.email.setValue('[email protected]'); } } |
- Modify the app.component.html file.
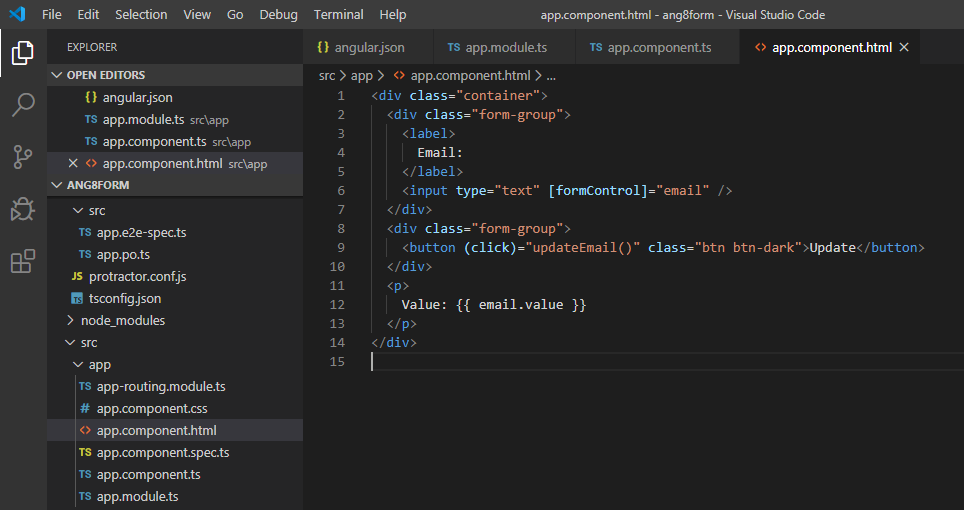
app.component.html:
<div class="container"> <div class="form-group"> <label> Email: </label> <input type="text" [formControl]="email" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <button (click)="updateEmail()" class="btn btn-dark">Update</button> </div> <p> Value: {{ email.value }} </p> </div> |
- Save the code.
- Start the server.
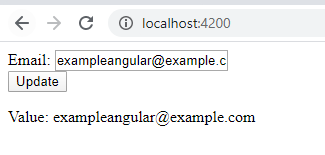
Output 1:
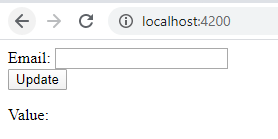
- Enter any email id.
- Check the result.
Output 2:
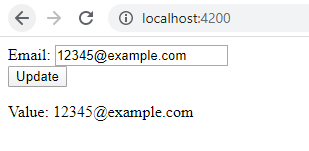
- Click on the “Update Email” button to update the email id as we saved in the template file.
Output 3: