All ArrayList LinkedList, and Vectors implement the List interface. Both (ArrayList and Vectors) use dynamically resizable arrays as their internal data structure. Whereas both ArrayList and Linked List are non synchronized. But they have several differences also, let us discuss ArrayList, LinkedList and Vectors in details with examples and differences.
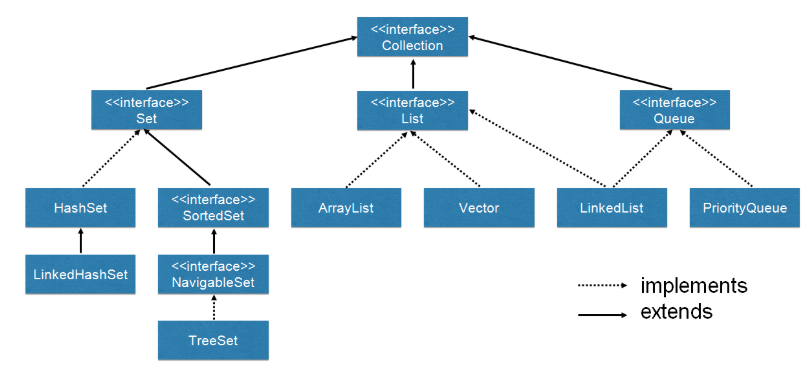
Collection Interface
ArrayList:
ArrayList in java, uses dynamic arrays to store its elements and maintains insertion order. ArrayList can store duplicate elements. It is a non synchronized collection type. ArrayList class extends AbstractList and implements the List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable interfaces.
Note: ArrayList provides the mechanism of random access because of it’s index based nature.
public class ArrayList extends AbstractList implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
Example
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { // ArrayList creation ArrayList javaDevelopers = new ArrayList(); // Adding elements to arraylist javaDevelopers.add("Shivanshu"); javaDevelopers.add("Roxy"); javaDevelopers.add("Ganesh"); javaDevelopers.add("Shailender"); // Traversing ArrayList elements System.out.println("Java Developrs:"); Iterator iterator = javaDevelopers.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } |
Output
Java Developrs:
Shivanshu
Roxy
Ganesh
Shailender |
LinkedList:
LinkedList in java, uses linked list data structure as it’s internal implementation to store elements. It can store duplicate elements. LinkedList class extends AbstractSequentialList and implements the List, Deque, Cloneable, Serializable interfaces. Like ArrayList, LinkedList is also not synchronized.
Note: LinkedList does not provides any facility like random access. Its performance is better than Arraylist on add and remove operations, but worse on get and set operations.
public class LinkedList extends AbstractSequentialList implements List, Deque, Cloneable, Serializable
Example
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { // LinkedList creation LinkedList javaDevelopers = new LinkedList(); // Adding elements to arraylist javaDevelopers.add("Shivanshu"); javaDevelopers.add("Roxy"); javaDevelopers.add("Ganesh"); javaDevelopers.add("Shailender"); // Traversing LinkedList elements System.out.println("Java Developres:"); Iterator iterator = javaDevelopers.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } |
Output
Java Developrs:
Shivanshu
Roxy
Ganesh
Shailender |
Vector
Vector class in java, implements a growable or dynamic array of objects. Similar to an array, Vector contains components which can be accessed using an integer index. After the Vector creation, the size of a Vector can grow or shrink as needed to accommodate adding and removing elements. Vector extends AbstractList and implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable interfaces.
public class Vector extends AbstractList implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
Example
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { // Vector creation Vector javaDevelopers = new Vector(); //Adding elements to vector javaDevelopers.addElement("Shivanshu"); javaDevelopers.addElement("Roxy"); javaDevelopers.addElement("Ganesh"); javaDevelopers.addElement("Shailender"); // Traversing vector elements System.out.println("Java Developrs:"); Enumeration enumeration = javaDevelopers.elements(); while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) System.out.println(enumeration.nextElement()); } } |
Output
Java Developrs:
Shivanshu
Roxy
Ganesh
Shailender |
ArrayListor or LinkedList?
ArrayList should be preferred over LinkedList if get and set are much more as compared to adding or removing the elements but if adding or removing operations are higher than get and set operation then LinkedList should be preferred.
Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList
| ArrayList | LinkedList |
| It uses a dynamic array as it’s internal implementation. | It uses doubly linked list as it’s internal implementation. |
| It is better in get and set operations. | It is better in adding and removing operations. |
Performance comparison between ArrayList and LinkedList
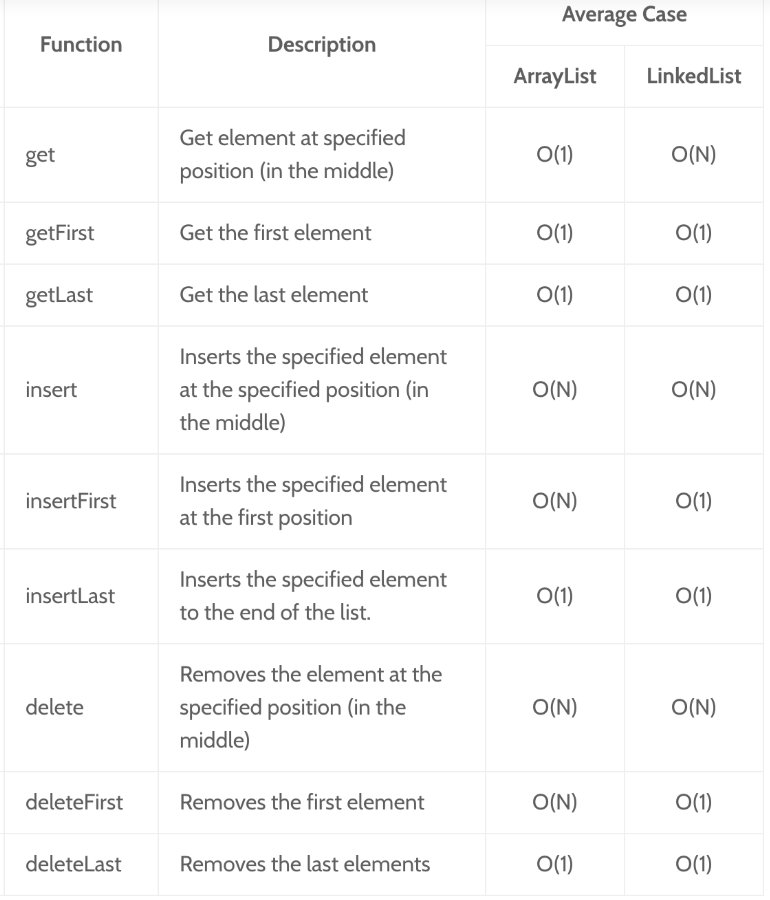
Example
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>(); // ArrayList add operation long startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { arrayList.add(i); } long endTime = System.nanoTime(); long duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("Time Taken by ArrayList in add operation: " + duration); // LinkedList add operation startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { linkedList.add(i); } endTime = System.nanoTime(); duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("Time Taken by LinkedList in add operation: " + duration); // ArrayList get operation startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { arrayList.get(i); } endTime = System.nanoTime(); duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("Time Taken by ArrayList in get operation: " + duration); // LinkedList get operation startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { linkedList.get(i); } endTime = System.nanoTime(); duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("Time Taken by LinkedList in get operation: " + duration); // ArrayList remove operation startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 9999; i >=0; i--) { arrayList.remove(i); } endTime = System.nanoTime(); duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("Time Taken by ArrayList in remove operation: " + duration); // LinkedList remove operation startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 9999; i >=0; i--) { linkedList.remove(i); } endTime = System.nanoTime(); duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("Time Taken by LinkedList in remove operation: " + duration); } } |
Output
Time Taken by ArrayList in add operation: 12505291 Time Taken by LinkedList in add operation: 8494106 Time Taken by ArrayList in get operation: 103500 Time Taken by LinkedList in get operation: 86634134 Time Taken by ArrayList in remove operation: 252982817 Time Taken by LinkedList in remove operation: 87576796 |
Vector or ArrayList?
As ArrayList is non-synchronized and fast, so in single threaded applications ArrayList should be preferred but in multi-threaded applications Vector should be used over ArrayList because of it’s synchronized nature.
Difference between ArrayList and Vector
| ArrayList | Vector |
| It is not synchronized. | It is synchronized. |
| It is not a legacy class. | It is a legacy class. |
| It increases its size by 50% of the array size. | It increases its size by doubling the array size i.e. 100%. |
| Iterator interface is used to traverse the ArrayList elements. | Iterator or Enumeration interface can be used to traverse the Vector elements. |
| ArrayList is much fast than Vector because it is non-synchronized. | Vector is slow as compared ArrayList because it is synchronized |
Java interview questions on collections
- What is the difference between arraylist and vector in java?
- What is the difference between arraylist and linkedlist?
- What is the difference between Iterator and ListIterator?
- What is the difference between Iterator and Enumeration?
- what is the difference between list and set in java?
- what is the difference between set and map in java?
- what is the difference between hashset and treeset in java?
- what is the difference between hashset and hashmap in java?
- what is the difference between hashmap and treemap in java?
- what is the difference between hashmap and hashtable in java?
- what is the difference between collection and collections in java?
- what is the difference between comparable and comparator interfaces?
- what is the hashcode method in java?
- Java equals method
- Java hashCode method
- Why to override hashcode and equals method in java?
- How hashmap works intrnally?
- How put and get works in hashmap?
- How to resolve collision in hashmap?
- How hashmap stores null key?
- How hashset works intrnally?