C# Multidimensional Arrays
Also known as rectangular arrays, a multi-dimensional array in C# can be either a two-dimensional array or a three-dimensional array. The data in a multi-dimensional array is stored in a tabular form, i.e, in the form of row * column, thus forming a matrix of elements. The comma is used inside the square brackets to create a multidimensional array.
Syntax Example:
int[,] a =new int[4,4]; //declaration of 2D array int[,,] a =new int[4,4,4]; //declaration of 3D array
Example:
using System; public class Example { public static void Main(string[] args) { int[,] a=new int[5,5]; //declaration of 2D array a[0,0]=1;//initialization of array a[1,1]=1; a[2,2]=1; a[3,3]=1; a[4,4]=1; //traversal of array for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ for(int j=0;j<5;j++){ Console.Write(a[i,j]+" "); } Console.WriteLine(); } } } |
Output:
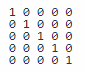
Explanation:
In the above example, we are declaring, initializing and traversing a two-dimensional array.
Declaration and initialization at the same time:
We can initialize a multidimensional array while declaration in C# using 3 ways.
Example: 1st way.
int[,] a = new int[3,3]= { { 10, 20, 30 }, { 40, 50, 60 }, { 70, 80, 90 } };
The array size can be omitted.
Example: 2nd way.
int[,] a = new int[,]{ { 10, 20, 30 }, { 40, 50, 60 }, { 70, 80, 90 } };
The new operator can also be omitted.
Example: 3rd way.
int[,] a = { { 10, 20, 30 }, { 40, 50, 60 }, { 70, 80, 90 } };
Example:
using System; public class Example { public static void Main(string[] args) { //declaration and initialization of array int[,] a = { { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 }, { 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 }, { 70, 80, 90, 10, 20 } }; //traversal of array for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ for(int j=0;j<5;j++){ Console.Write(a[i,j]+" "); } Console.WriteLine(); } } } |
Output:

Explanation:
In the above example, we are creating a multidimensional array and initializing it at the time of declaration.