C# Strings
To represent a sequence of characters, strings are used in C#. It is an object of System.String class. Several operations like concatenation, comparison, getting substring, search, trim, replacement etc, can be performed on C# strings.
Comparison between string and String:
The string is an alias for System.String class. It is a keyword in C# which is equivalent to String. Any naming convention can thus be used for a string in C#.
Example: To create a string using the string keyword:
string s1 = "keyword";
Example: To create a string using the String class:
String s2 = "class";
Example:
using System; public class Example { public static void Main(string[] args) { string str1 = "String1"; char[] ch1 = { 'S', 't', 'r', 'i', 'n', 'g', '2' }; string str2 = new string(ch1); Console.WriteLine(str1); Console.WriteLine(str2); } } |
Output:
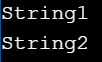
Explanation:
In the above example, we are creating two strings in C# using the string keyword. Both the strings will be displayed on the console screen as output.
C# String methods:
C# provides several methods to be used for performing operations on a string or strings. Below we are listing all the important C# String methods. The uses of these methods were also described below.
| Method | Uses |
| Clone() | To get a reference to this instance of String. |
| Compare(String, String) | To compare two specified String objects to get an integer which represents their relative position in the sorted order. |
| CompareOrdinal(String, String) | To compare two specified String objects. The numeric values of the corresponding Char objects in each string is evaluated. |
| CompareTo(String) | To compare this instance with a specified String object to determine whether this instance precedes, follows, or appears in the same position in the sort order as the specified string. |
| Concat(String, String) | To concatenate two specified instances of String. |
| Contains(String) | To get a value determining whether a specified substring occurs within this string. |
| Copy(String) | To create a new instance of String with the same value as a specified String. |
| CopyTo(Int32, Char[], Int32, Int32) | To copy a specified number of characters from a specified position in this instance to a specified position in an array of Unicode characters. |
| EndsWith(String) | To verify that the end of this string instance matches the specified string. |
| Equals(String, String) | To verify that two specified String objects have the same value. |
| Format(String, Object) | To replace one or more format items in a specified string with the string representation of a specified object. |
| GetEnumerator() | To retrieve an object that can iterate through the individual characters in this string. |
| GetHashCode() | To get the hash code for this string. |
| GetType() | To return the Type of the current instance. |
| GetTypeCode() | To get the TypeCode for class String. |
| IndexOf(String) | To report the zero-based index of the first occurrence of the specified string in this instance. |
| Insert(Int32, String) | To get a new string in which a specified string is inserted at a specified index position. |
| Intern(String) | To get the system’s reference to the specified String. |
| IsInterned(String) | To get a reference to a specified String. |
| IsNormalized() | To define that this string is in Unicode normalization form C. |
| IsNullOrEmpty(String) | To define that the specified string is null or an Empty string. |
| IsNullOrWhiteSpace(String) | To define whether a specified string is null, empty, or consists only of white-space characters. |
| Join(String, String[]) | To concatenate all the elements of a string array. The specified separator is used between each element. |
| LastIndexOf(Char) | To indicate the zero-based index position of the last occurrence of a specified character within String. |
| LastIndexOfAny(Char[]) | To indicate the zero-based index position of the last occurrence in this instance of one or more characters specified in a Unicode array. |
| Normalize() | To get a new string whose textual value is the same as this string. The binary representation is however in Unicode normalization form C. |
| PadLeft(Int32) | To get a new string that right-aligns the characters in this instance by padding them with spaces on the left. |
| PadRight(Int32) | To get a new string that left-aligns the characters in this string by padding them with spaces on the right. |
| Remove(Int32) | To get a new string in which all the characters in the current instance, beginning at a specified position and continuing through the last position, have been deleted. |
| Replace(String, String) | To get a new string in which all occurrences of a specified string in the current instance are replaced with another specified string. |
| Split(Char[]) | To split a string into substrings based on the characters in an array. |
| StartsWith(String) | To verify whether the beginning of this string instance matches the specified string. |
| Substring(Int32) | To get a substring (starting at a specified character position and continuing to the end of the string) from this instance. |
| ToCharArray() | To copy the characters in this instance to a Unicode character array. |
| ToLower() | To convert a String into lowercase. |
| ToLowerInvariant() | To convert String into lowercase using the casing rules of the invariant culture. |
| ToString() | To get an instance of String. |
| ToUpper() | To convert String into uppercase. |
| Trim() | To eliminate all the leading and trailing white-space characters from the current String object. |
| TrimEnd(Char[]) | To eliminate all the trailing occurrences of a set of characters specified in an array from the current String object. |
| TrimStart(Char[]) | To eliminate all the leading occurrences of a set of characters specified in an array from the current String object. |