The term calorific value is also known as the energy that is gained by the human body from the foodstuff. The energy requirements of the body are dependent on gender, age, weight, and many other factors. The calorific value is measured in the kilo joule (KJ) and the kilo calorie (Kcal).
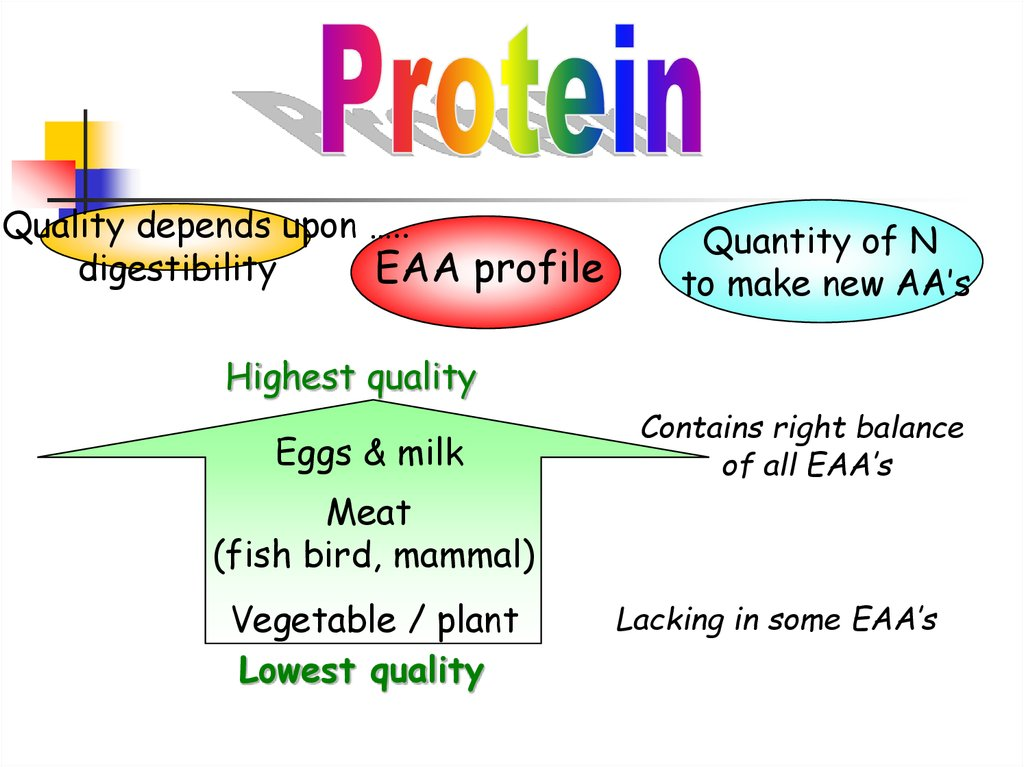
Proteins are essential molecules for the health and it has the top status for human nutrition. Human and all other living organisms must have to intake the minimum of the required amount of proteins for driving their muscles and to sustain their living. Proteins are an essential part of the food. For the human body, the proteins are the most versatile molecules and play a key role in all the biological processes.
Proteins Provides Energy for Body
The animal proteins provide all the essential amino acids which are required by the human body. The consumption of proteins is much helpful to reduce the weight and minimize the gain in weight. About 25-30% of daily intake of the protein calories boosts up the metabolism up to 80 -100 calories per day, 25% calories of the proteins bring the feel of fullness and reduced the thoughts about food up to 60%. A modest increase in protein calories from 15-18% causes a significant reduction in body fats. The calorific value of proteins can help to gain muscle strength. In other words, it maintains the net protein balance or nitrogen balance in the body as proteins are rich in the nitrogen contents.
How Much Calorific Value is Required from Proteins?
For calculating the average daily intake of the proteins, the ratio of the 1 gram of the protein is used for every kilogram of the weight of the person. Being physically active can increase the protein requirements of the body. According to a study following protein levels are required for the varying activities.
For the minimal activity levels, 1 g of protein is required for every one kg of body weight.
For moderate activity levels, 1.3 g of protein is required for every one kg of the body weight.
For the intense activity levels, 1.6 g of protein is required for one every kg of the body weight.
Maintenance of Optimum Calorific Value of Proteins
Typically, daily, people can only consume 2 g of proteins per one kg of their body weight without having any significant side effects. For some athletes, this level can be increased up to 3.5 grams. The production of much energy from proteins may cause dehydration, irritability, nausea, headache, diarrhea, unexplained exhaustion, and intestinal discomfort.