All organisms are composed of a single cell and are called unicellular organisms while others are many cells called multicellular organisms.
Cell
- The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
- The branch of biology that deals with the structural and functional organization of cells is called cell biology or cytology.
Discovery of Cell



- Jan Swammerdam was the first person to describe a cell (in 1658).
- The actual existence of cytology came with the discovery of cell in 1665 by Robert Hooke, an English botanist.
- So he is also considered as the Father of Cytology.
- He coined the term ‘cell’ to design the hollow cavities which he observed in the section of a cork tissue (cellula (Latin) – little rooms).
- Hooke had seen only the cell walls and he ignored the existence of substances within the cell wall. He did not realize its true nature and significance.
- During the 17th century, Anton van Leeuwenhock (1632 – 1723) discovered the animalcules, protozoa, bacteria etc.
- In the beginning of the 19 century, considerable discoveries were made in cell biology. So this period is described as the “classical era of cytology“.
- During this period almost all the cell organelles were discovered.
CELL THEORY
The German botanist Matthias Schleiden and the German physiologist Theodor Schwann independently proposed the cell theory or cell doctrine in 1838 and 1839 respectively.
- Matthias Schleiden observed that all plants are composed of different kinds of cells which form the tissues of the plant.
- Theodor Schwann reported that cells had a thin outer layer which is currently known as the ‘plasma membrane’.
- In 1858, Rudolf Von Virchov supplemented the cell theory by stating that all new cells originate only from pre- existing cells by division.

The postulations of cell theory are:
- All the organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic organizational unit of life.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
AN OVERVIEW OF CELL
Each cell is as a self contained unit. It carries out all the biological activities independently.
The basic structure of a cell is as follows:
- It has an outer membrane as the delimiting structure of the cell.
- Inside each cell is a dense membrane bound structure called nucleus. This nucleus contains the chromosomes which in turn contain the genetic material, DNA or RNA.
- A semi-fluid matrix called cytoplasm occupies the volume of the cell
- There are certain membrane bound distinct structures called organelles inside the cell.
The shape of cells can vary greatly. The smallest cell so far observed is a single celled oorganism called Mycoplasma (0.3 μm in length). The largest cell is the egg of an ostrich.
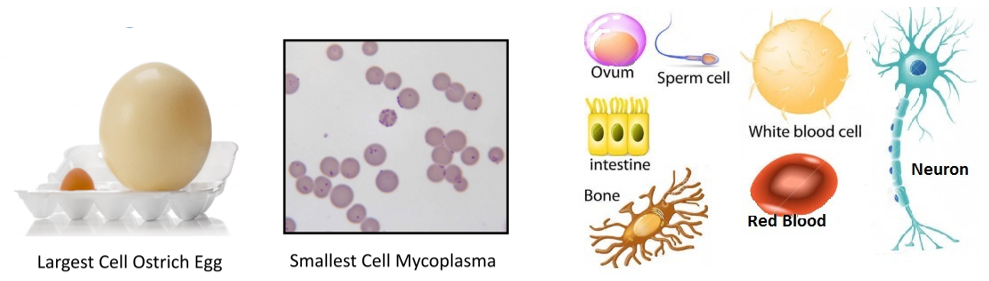
Cells also vary greatly in their shape. They may be disc-like, polygonal, columnar, cuboidal, thread like, or even irregular. The shape of the cell may vary with the function they perform.
Functions of a Cell
- It releases energy by the breaking of food molecules. With the help of that energy the cell synthesizes complex molecules.
- Each cell reproduces itself and has its own life cycle.
- The cell regulates and maintains its own activities and physiochemical conditions.