The characteristic features of Aves (birds) are the presence of feathers and most of them can fly except flightless birds (e.g., Ostrich).
Examples:
 |
 |
 |
| Corvus (Crow) | Columba (Pigeon) | Psittacula (Parrot) |
 |
 |
 |
| Struthio (Ostrich) | Pavo (Peacock) | Aptenodytes (Penguin) |
Body characteristics:
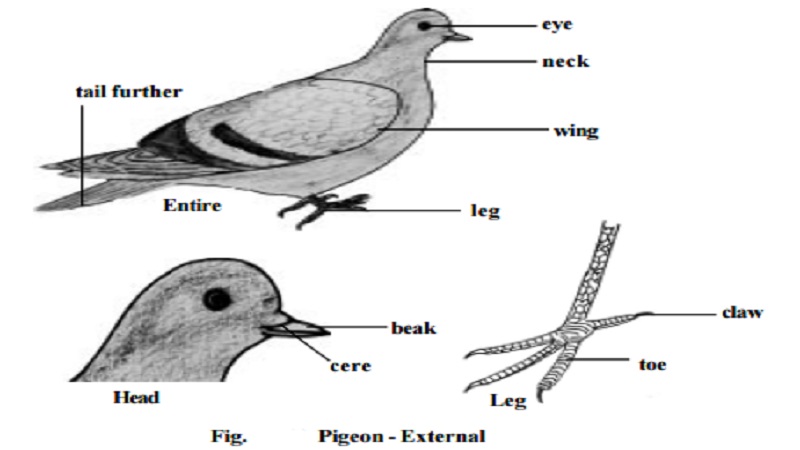
- They have a streamlined body that helps them to fly.
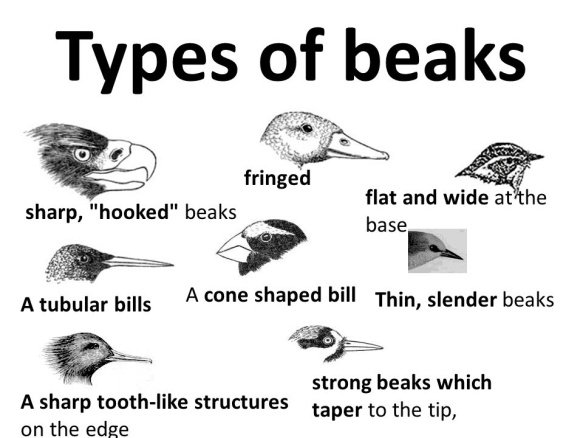
- The jaws are modified into beak. Teeth are absent. The beak has various shapes and size, adapted for different food habits.
- The body is covered by feathers.
- The forelimbs are modified into wings. Flight muscles are well developed to assist the movement of wings.
- The hind limbs generally have scales and are modified for walking, swimming or clasping the tree branches.
- Skin is dry without glands except the oil gland at the base of the tail.
- Voice box, called syrinx, is present.
- Endoskeleton is fully ossified (bony). Bones are hollow and have air cavities (pneumatic). It makes the body light, adapted for flying.
Physiology:
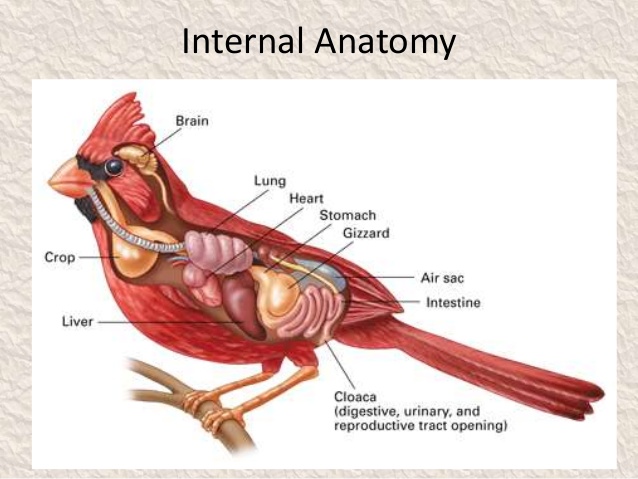
- The digestive tract of birds has additional chambers, the crop and gizzard.
- Heart is completely four–chambered.
- They are warm-blooded (homoiothermous) animals, i.e., they are able to maintain a constant body temperature.
- Respiration is by lungs. Air sacs connected to lungs supplement respiration.
Reproduction: Sexes are separate. Fertilisation is internal. They are oviparous and development is direct. Eggs have a calcareous shell.