The term reptilia is derived from the Latin word repere or reptum, which means to creep or crawl. Hence, the class name refers to their creeping or crawling mode of locomotion.
Habitat: They are mostly terrestrial animals.
Examples:
 |
 |
 |
| Chelone (Turtle) | Chameleon (Tree lizard) | Crocodilus (Crocodile) |
 |
 |
 |
| Testudo (Tortoise) | Calotes (Garden lizard) | Alligator (Alligator) |
 |
 |
 |
| Naja (Cobra) | Bangarus (Krait) | Vipera (Viper) |
Body characteristics:
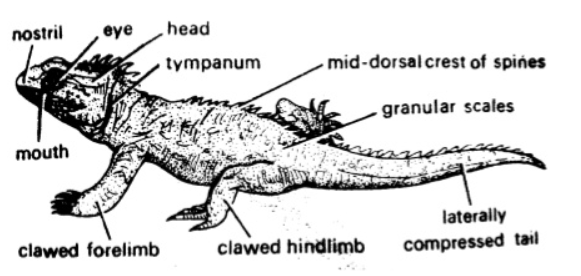
- The body is divided into head, neck, trunk and trail.
- The skin is dry and devoid of any glands. It is covered by horny epidermal scales (or scutes).
- They do not have external ear openings. Tympanum represents the ear. It is very small and depressed.
- They have 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
- Trunk bears two pairs of pentadactyl limbs with clawed digits.
- Heart is usually three-chambered, but four-chambered in crocodiles.
Physiology: Reptiles are poikilotherms. Snakes and lizards shed their scales as skin cast. Respiration is through lungs.
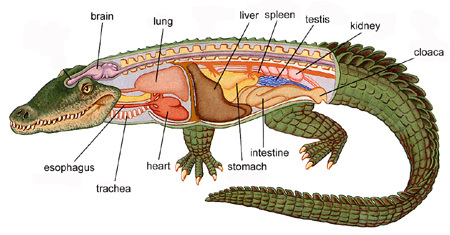
Reproduction: Sexes are separate. Fertilisation is internal. They are oviparous and development is direct. Eggs are covered by a hard calcareous shell.