Lymph can be described as a mobile connective tissue comprising lymph plasma (fluid) and lymph corpuscles (cells). These lymph compositions can detail explain below
- Lymph Plasma: This is similar to that of blood but has very few blood proteins, less calcium and phosphorus, and high glucose concentration. Mainly globulin proteins are available which are actually antibodies. The other components of the lymph plasma are like that of blood plasma, eg organic, inorganic substances, water and so on.
- Lymph Corpuscles: These are seen as the floating amoeboid cells, the leucocytes (white blood corpuscles), that are mostly lymphocytes. Erythrocytes (red blood corpuscles) and platelets are absent in lymph.
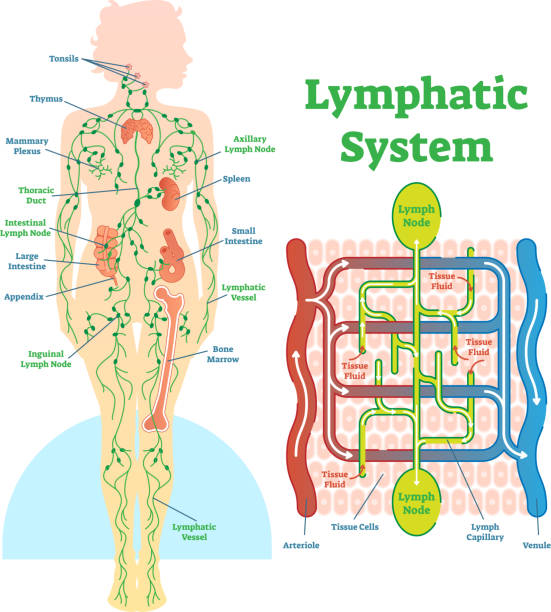
- Lymphoid Organs: The organs are the last composition which secretes lymph are called lymphoid organs. Asides the lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus gland, spleen and Peyer’s patches are the other lymphoid organs. The spleen is classified as the largest mass of lymphatic tissue in the body. Now study the functions of lymph one after the other.
Functions of Lymph
The following are some of the functions which can be seen under lymph
- The first function is that Lymph acts as a “middle man” which transports oxygen, food materials, hormones, and so on., to the body cells and brings carbon dioxide and other wastes products, from the body cells to blood and then finally pours the same into the venous system.
- Secondly, Body cells are kept moist by the lymph.
- In the same vain Lymph nodes produce lymphocytes. Lymph takes lymphocytes and antibodies from the lymph nodes directly to the blood.
- Lymph destroys the invading microorganisms and foreign particles in the lymph nodes.
- Lymph also absorbs and transports fat and fat-soluble vitamins from the intestine. Lymphatic capillaries available in the intestinal villi are called lacteals which are associated with absorption and transportation of fat and fat-soluble vitamins.
- Like Wise lymph brings plasma protein macromolecules synthesized in the liver cells and hormones produced in the endocrine glands to the blood. These molecules cannot go through the narrow blood capillaries but can diffuse into the lymphatic capillaries.
- Last but not the least Lymph keeps the volume of the blood. As soon as the volume of the blood decrease in the blood vascular system, the lymph rushes from the lymphatic system to the blood vascular system. These functions and explained functions make lymph to seen as being important in the body system.