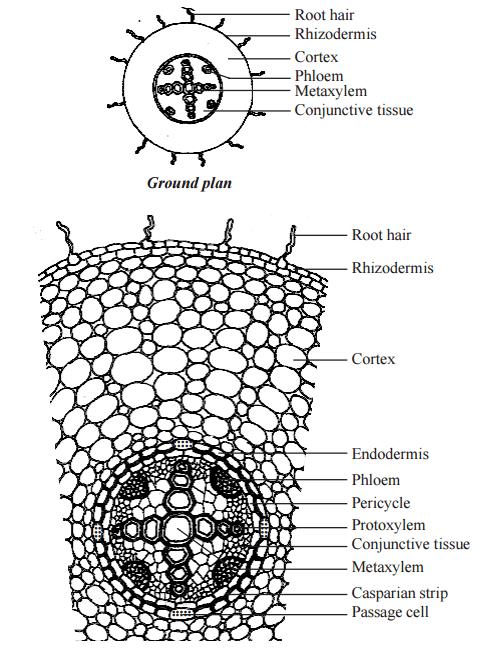
Epidermis
- The outermost layer of a dicot root is called epiblema or piliferous layer.
- It is made of a single layer of parenchyma cells.
- The cells have tubular outgrowths called root hairs.
- Cuticle and stomata are absent.
Cortex
- it is the region between epidermis and endodermis.
- It is homogeneous and is composed of loosely arranged parenchyma cells.
Endodermis
- It is the innermost layer of cortex.
- It is composed of a single layer of barrel-shaped cells.
- The radial walls of the cells have casparian strips due to the deposition of suberin.
Stele
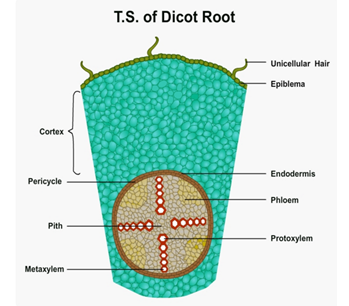
- Stele is the central part of the root.
- It is very small when compared to the size of the cortex.
- It is composed of the vascular tissue and the intrastelar ground tissue.
- Pericycle is the outermost layer of stele.
- It is composed of a single layer of parenchymatous cells.
- Growth of lateral roots and vascular cambium during secondary growths takes place in these cells.
- Pith is very small and inconspicuous.
- Vascular bundles are seen in the central position.
- They have radial arrangement. It is a characteristic feature of roots.
- Protoxylem is seen towards the periphery, and metaxylem towards the centre. Hence, the xylem is exarch. This is also a characteristic feature of roots.
- The parenchymatous cells found between the xylem and phloem is known as conjective tissue.