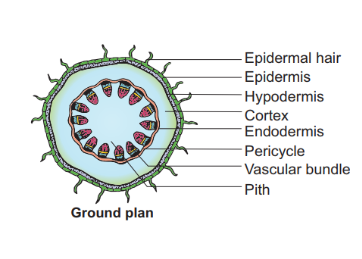
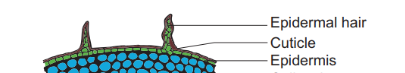
Epidermis
- It is the outermost layer formed of a single layer of cells.
- It forms the protective layer of the stem.
- It has a thick waxy layer called cuticle over the external surface.
- It bears trichomes and a few stomata.
Cortex
- The cortex is heterogeneous and differentiated into several sub- zones.
- The outer zone is called hypodermis and is composed of a few layers of collenchymas cells. It provides mechanical strength to the stem.
- The middle cortical layers are composed of thin walled chlorenchyma and parenchyma cells.
- The innermost layer is the endodermis. It is single layered, composed of barrel-shaped cells and rich in starch grains. Hence it is also called starch sheath.
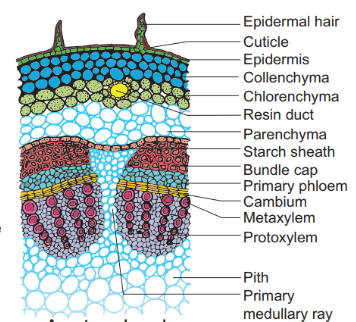
Pericycle
- It is the region between the endodermis and the vascular bundle.
- It occurs in the form of semilunar patches of sclerenchyma cells.
- Since it is found above the vascular bundle, it is also known as bundle cap.
Vascular bundles
- They are few in number, and are arranged in the form of a ring.
- They are conjoint, open (cambrium present) with endarch protoxylem.
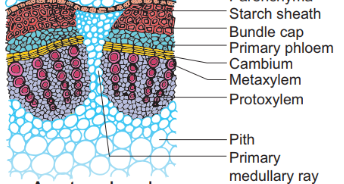
Medullary Rays
- It is composed of a few layers of elongated cells lying between two vascular bundles.
- It acts as a pathway for the radial conduction of food and water.
Pith
- It is the central portion of the ground tissue.
- It is composed of loosely arranged parenchyma cells.
- Their main function is storage.
