Fingerprinting could be a chemical check that shows the genetic makeup of an individual or different living things.It’s used as proof in courts, to spot bodies, capture blood relatives, and to seem for cures for sickness.
Genetic makeup
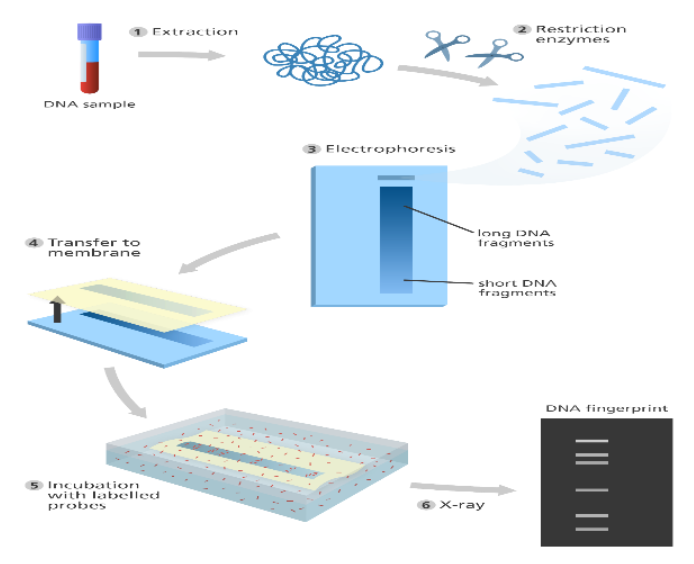
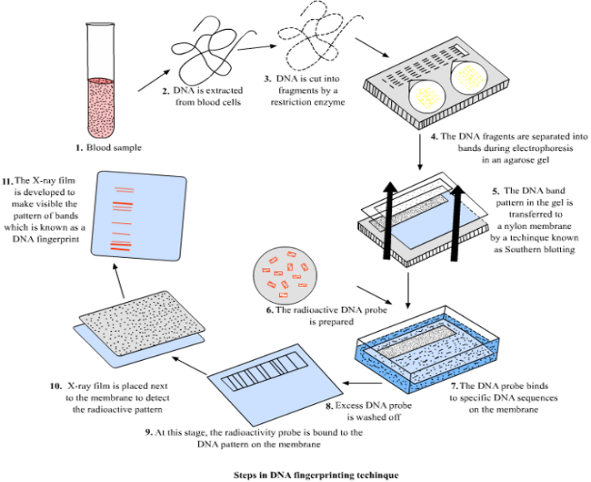
DNA process uses chemicals to separate strands of deoxyribonucleic acid and reveal the distinctive elements of your ordination.The results show up as a pattern of stripes which will be matched against different samples.
These compounds are called bases, and there are 4 of them.
They combine up with another to create what are referred to as base pairs. Your deoxyribonucleic acid has regarding three billion of those couples. The way they’re strung together tells your cells how to make copies of each other. The complete set of your compounds is known as a genome.
DNA fingerprinting uses chemicals to split the strands of DNA and show the unique parts of your genome.Pattern of stripes shows up as a result that can be matched against many other samples.
Uses
It can: Physically connect a bit of proof to an individual or rule out somebody as a suspect.
Show United Nations agency your folks, siblings, and different relatives, also identify a dead body that’s too old or damaged to be recognizable. DNA fingerprinting is extremely accurate. Most countries now keep DNA records on file in much the same way police keep copies of actual fingerprints. It also has medical uses. It can: Match tissues of organ donors with those of people who need transplants.
Identify diseases that area unit passed down through your family.
Help notice cures for those diseases, referred to as hereditary conditions.
Fingerprint Test
To get your genetic fingerprint, you’d provides a sample of cells from your body.
This can come back from a swab within your mouth, from your skin, the roots of your hair, or your secretion, sweat, or different body fluids. Blood is usually the easiest way. Lab workers treat the sample with chemicals to separate the DNA, which is then dissolved in water. Your deoxyribonucleic acid is dig smaller segments with another activity to urge sections of five to 10 base pairs that repeat themselves.
Technicians copy those little sections ample times to form the samples longer for easier study.Lab staff take those strips of deoxyribonucleic acid and blend them into a gel.Then they run an electrical current through the gel that separates smaller strands of deoxyribonucleic acid from the larger ones.
A dye additional to the gel makes the deoxyribonucleic acid strips stand out once they’re placed against Associate in Nursing ultraviolet radiation or lit up with an optical maser. The more these short segments are tested, the more accurate the DNA profile will be. The strips will show a barcode-like pattern that can then be compared to the results from another sample of DNA to find a match.