p-Block Elements: Group 17 (Electronic configuration)
Electron structure of the halogens
Fig 1: Arrangement of electrons in the first three elements of the halogen family.
Table 1: Electronic configuration of group 17 elements.
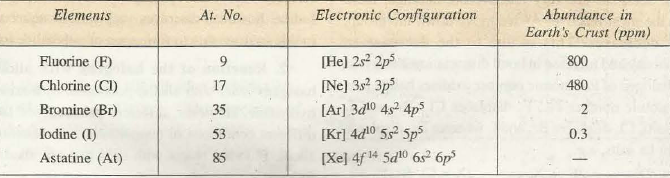
All halogens have seven electrons in their outermost shell comprising completely filled s orbital and p orbital with 5 electrons. They can easily obtain a full octet by gaining one electron. The general electronic configuration is ns2np5 and the last electron occupies p orbital. These elements are a part of the p block. They obtain the octet by accepting one electron to produce a univalent anion, X– (F–, Cl–, Br– and I–). They share unpaired electrons to form covalent bonds as well. Hence, they are monovalent with common valency of -1.Fluorine is the most reactive halogen because the electron it is attracting is coming into a shell closest to the positive nucleus. There is more attraction which makes it easier to gain an extra electron. The electron when reaching the fluorine octet stays intact due to closeness to the nucleus. Therefore fluorine is the most reactive and it produces stable ionic salts and covalent compounds due to highest electronegativity.
The rows in the periodic table show increasing energy levels and the levels rise as one moves up the list of halogens. Fluorine, on row 2, has a valence-shell configuration of 2s 2 2p 5; while that of chlorine is 3s 2 3p 5. Note that only the energy level changes, but not the electron configuration at the highest energy level. The same goes for bromine (4s 2 4p 5 ), iodine (4s 2 4p 5 ), and astatine (5s 2 5p 5 ).Thus it is ironic that they are neighbors to the Group 8 noble gases, the least reactive among the elements.
Table 2: Reaction of halogens with iron wool
| Halogen | Reaction with iron wool |
|---|---|
| Fluorine | Reacts with almost anything instantly. Very few scientists handle fluorine because it is so dangerous. |
| Chlorine | Reacts with heated iron wool very quickly. |
| Bromine | Must be warmed and the iron wool heated. The reaction is faster. |
| Iodine | Must be heated strongly and so does the iron wool. The reaction is slow. |
Halogens gain an electron in reactions to form negative ions with a -1 charge and they are 1 electron less than a full octet. All the Group 17 elements are molecules containing two atoms. By sharing electrons in a covalent bond full outer electron shells are achieved. The atoms of each element gain more shells and increase in size going down the group. Likewise, the outer shell moves further from the nucleus. This results in the valence shell being shielded by more inner electron shells. As the outer shell moves further from the positive attraction of the nucleus, attraction towards incoming electron decreases due to overall reduced negative charge on the atom. Therefore, astatine is a metalloid which prefers sharing or losing electrons to become an unstable and radioactive compound.