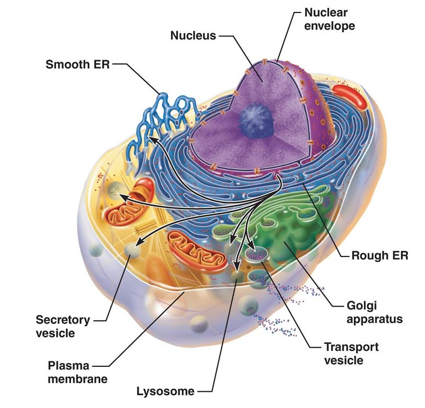
The Endomembrane system includes
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi complex
- Lysosomes and
- Vacuoles.
The functions of these organelles are well coordinated.
Endoplasmic reticulum
- The Endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membrane bound cavities, vesicles and tubules distributed throughout the cytoplasm.
- It is the cytoskelteon of the cell.
- The name Endoplasmic reticulum was coined by Porter.
- ER divides the intracellular space into two distinct compartments, i.e., luminal (inside ER) and extra luminal (cytoplasm) compartments.
- It is absent in prokaryotes, egg and embryonic cells
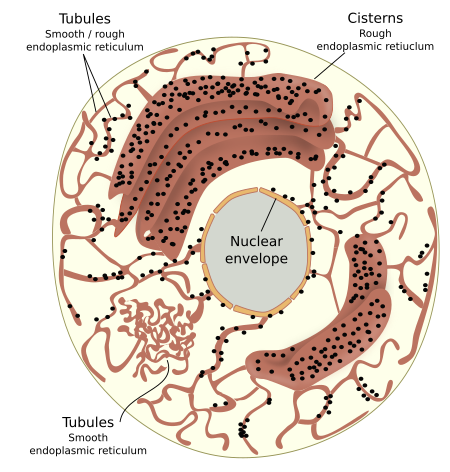
- It consists of three components
- Cisternae: These are long, flattened, un-branched sac like structures arranged as parallel bundles. They have ribosomes on their surface and are normally found in secretory cells
- Vesicles: These are rounded or ovoidal structures.
- Tubules: These are smooth walled and highly branched tubular spaces having diverse forms. They normally occur in non-secretory cells.
- The membrane of E.R. is continuous with plasma membrane, Golgi membrane and nuclear membrane.
- The lumen of ER acts as a passage for the intracellular transport of secretory products.
ER is classified into two types.
Granular or Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
- In some ER, spherical granular structures called ribosomes are attached on the surface.
- This type of ER is called Rough ER
- It occurs in almost all cells which are actively engaged in protein synthesis
Agranular or Smooth Endoplasmic Retuculum (SER)
- Here ribosomes are not attached with the ER and the surface is smooth.
- It is developed in cells that synthesize steroid hormones.
- The SER is the major site for synthesis of lipid.
- The ER present in retinal cells is called myeloid bodies.
- The ER present in muscle cells are called sacroplasmic reticulum.
Functions
- It functions as a cellular circulatory system.
- It synthesizes several steroid hormones, enzymes and cholesterol.
- The rough ER synthesizes protein with the help of ribosomes
- It produces microbodies.
- Metabolic waste products are detoxified by smooth ER.
- It helps in the formation of middle lamella and nuclear membrane