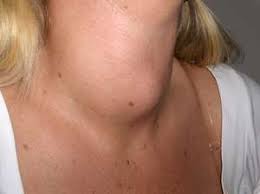
Exophthalmic goiter, also referred to as graves’ disease or toxic diffuse goiter, is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. In exophthalmic goiter, there is excessive secretion of thyroid hormone accompanied by enlargement of the thyroid gland. The increased production of the thyroid hormone may result in signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
Causes
The thyroid gland is an important part of the endocrine system as it releases hormones that help keep the body metabolism running. A chemical known as thyroid stimulating hormone(TSH) produced in the pituitary glands informs the thyroid gland how much hormones to produce. In exophthalmic goiter, the immune system produces antibodies that trigger the TSH receptor making the thyroid gland produce too much hormones. This speeds up metabolism. In exophthalmic goiter, the body’s is tricked into releasing excessive hormones causing hyperthyroidism. The exact cause of this is not known. However, research shows that it may be caused by a combination of environmental factors such as smoking and genetic factors which includes a family’s history of the disease.
Symptoms
Exophthalmic goiter involves overproduction of thyroid hormones which has a variety of effects on the body. Symptoms include
- Weight loss
- Hand tremors
- Nervousness
- Changes in menstrual cycle
- Anxiety and irritability
- Erectile dysfunction
- Increased sweating
- An irregular heartbeat
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
Treatment
Treatment for exophthalmic goiter majorly aim at reducing the overproduction of the thyroid hormone and reducing the symptoms of the disease. The treatment includes;
Anti thyroid medication
Anti thyroid medication helps in blocking the oxidation iodine in the thyroid glands thus preventing them from producing excessive amounts of thyroid hormones.
Radioactive iodine therapy
Radioactive iodine is orally taken to destroy any overactive thyroid cells thus prevent over production of thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland uses iodine to produce thyroid hormones. Taking the radioactive iodine orally builds it up in the thyroid gland destroying the overactive thyroid cells.
Surgery
With the improvement of other modes of treatment of the disease, surgery is the least common. Surgery is done to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. It is advantageous because it is the fastest and permanent way to restore normal levels of the thyroid hormones. Part of the thyroid gland may be removed allowing the remaining portion to continue with the functions. Removal of the whole of the thyroid gland will render the body unable to produce enough thyroid hormones. This condition is known as hypothyroidism and thyroid hormone pills may be recommended to perform the functions of the hormone.
Beta blockers
Beta blockers can help reduce the symptoms of exophthalmic goiter. They are mostly used alongside other treatments to help alleviate the symptoms but not as treatment.