Expected exception test is used for the methods which can throw an exception. We have to specify expected exception in @Test(expected = expectedException.class) action. If expected exception or any of its subclass exception is thrown by the method then JUnit will pass this unit test.
Example:
DivisionTestCase.java
import com.w3schools.business.*; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import org.junit.Test; /** * This is test case class for division method. * @author w3schools */ public class DivisionTestCase { //DivisionTest class objects DivisionTest divisionTest1 = new DivisionTest(10, 2); DivisionTest divisionTest2 = new DivisionTest(10, 0); //Test case for division @Test public void test() { assertEquals(5, divisionTest1.division()); } //Test case for expected ArithmeticException, //As in this case ArithmeticException // is the expected exception so JUnit //will pass this unit test. @Test(expected = ArithmeticException.class) public void testException() { assertEquals(5, divisionTest2.division()); } } |
DivisionTest.java
/** * This is simple java class containing division method. * @author w3schools */ public class DivisionTest { //data members int num1, num2; //parameterised constructor public DivisionTest(int num1, int num2){ this.num1 = num1; this.num2 = num2; } //division method public int division() throws ArithmeticException{ return num1/num2; } } |
Output:
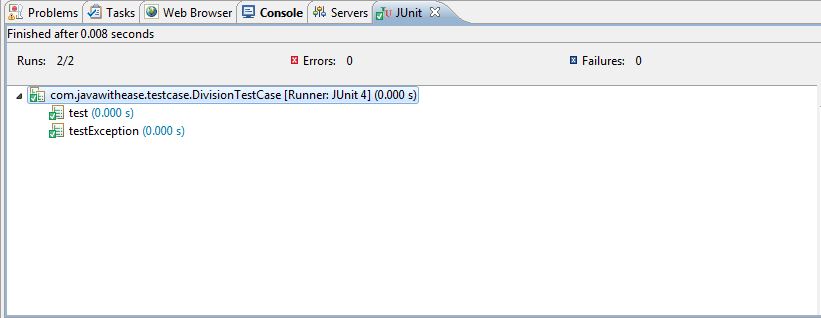
Download this example.
Next Topic: Junit ignore test.
Previous Topic: Junit basic annotation example.