Flower is the reproductive part of a plant. It is a modified shoot with very short and condensed internodes and a number of floral appendages at each node. These floral appendages are modified leaves. A flower may be trimerous, tetramerous or pentamerous when the floral appendages are in multiple of 3, 4 or 5, respectively.
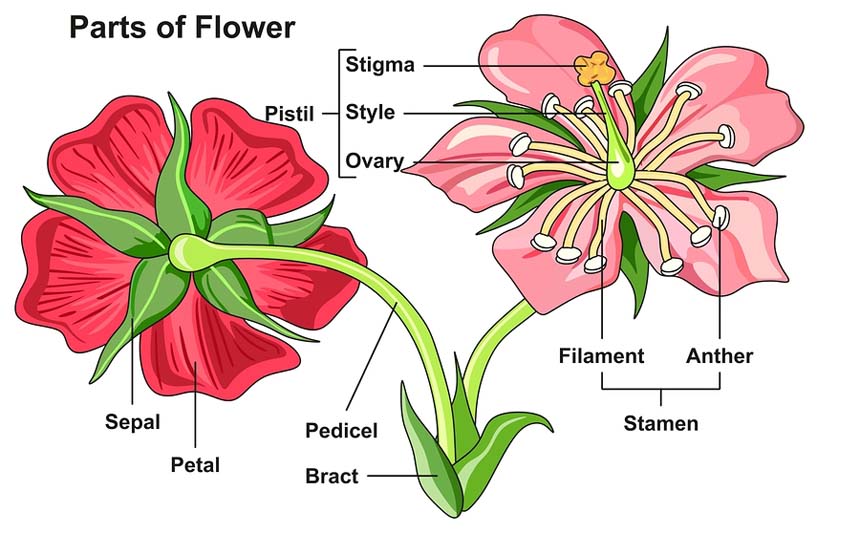
- Flowers can be Axilliary or terminal in position.
- They are produced on the axils of modified leaf called bract.
- Flowers with bract are called bracteates and those without bract are called ebractate.
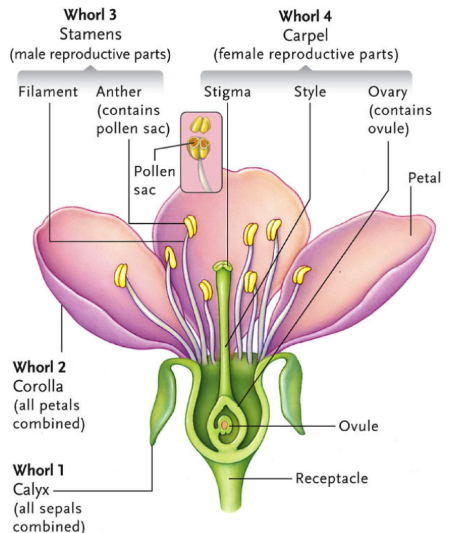
Whorls of a Flower
- The floral appendages are arranged in whorls on the swollen end of the pedicel called thalamus or receptacle.
- A complete flower contains four whorls: Calyx, Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium.
- The flower is incomplete when one or more whorls are missing.
- The whorls are classified into 2 groups.
- Accessory whorls: They are the outer whorls – calyx and corolla. Calyx (sepals) is a protection organ while corolla (petals) is the attractive organ. In some flowers, the calyx and corolla are not distinct, and is known as the perianth.
- Essential whorls: They are the inner two whorls – Androecium (stamens) and Gynoecium (ovary). They are the reproductive structures of the flower. If a flower has both androecium and gynoecium, it is called a bisexual flower. If either one of these is only present in the flower, it is called a unisexual.
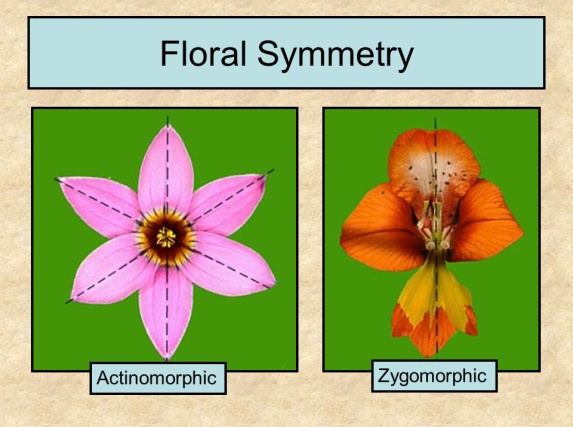
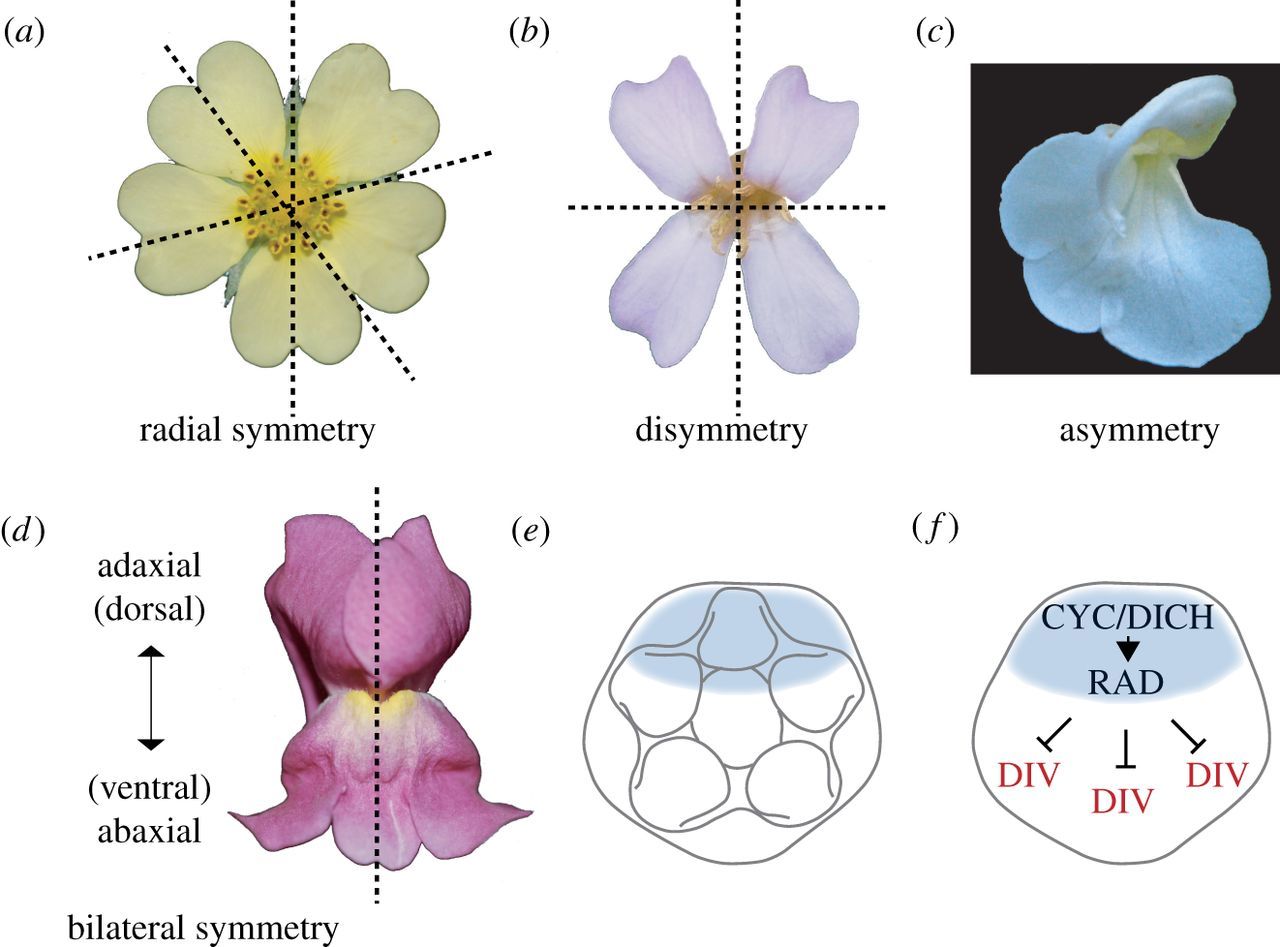
Symmetry in Flowers
- Flowers that can be divided into two equal halves along any median longitudinal plane are called Actinomorphic (or regular) flowers. (e.g. Hibiscus, Ixora)
- If the flowers can be divided into two equal halves only in one vertical plane, they are called Zygomorhic flowers. (e.g. Pisum)
- Flowers that cannot be divided into two similar halves are called asymmetrical flowers.
Based on the position of the floral parts on the thalamus, flowers are grouped into three types.
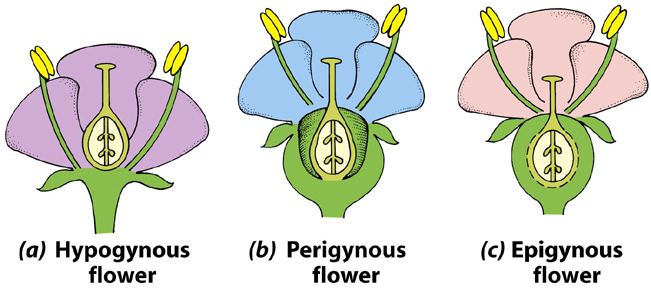
Hypogynous flowers:
- In this flower, the gynoecium occupies the highest position.
- The thalamus may be conical or flat.
- The ovary is above the level of thalamus.
- The rest of the whorls – sepals, petals and stamens, are arranged below the ovary.
- The ovary is thus called superior ovary. (e.g. Hibiscus)
Perigynous flower:
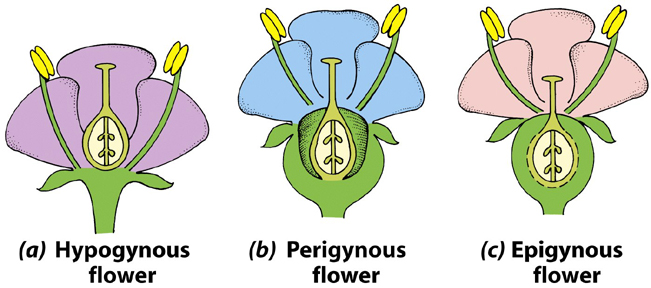
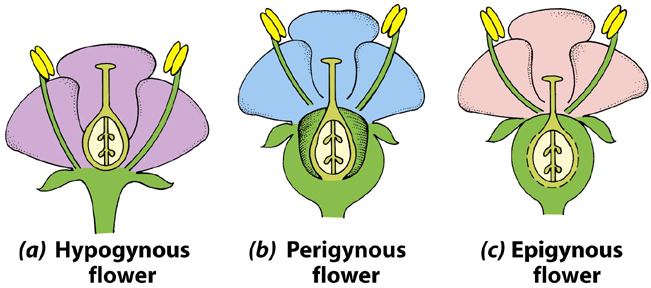
- The thalamus grows upwards forming a cup-shaped structure enclosing the ovary.
- The other floral parts are located at the rim of the thalamus.
- Thus, the ovary is called half-superior or half-inferior ovary. (e.g. Rose)
Epigynous flower:
- The margin of the thalamous grows upwards, and encloses the ovary completely.
- From the margin, other floral parts will arise.
- Thus, the ovary is called inferior ovary. (e.g. Ixora)