The body control and coordination in frogs are carried out by nervous system and the endocrine glands.
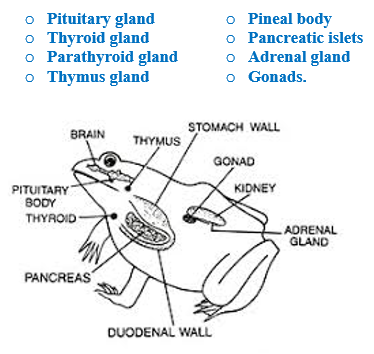
Endocrine glands
- Endocrine glands are responsible for the chemical coordination in frogs.
- It is carried out by the secretions of these glands called hormones.
- The major endocrine glands found in a frog are
Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into
- CNS – Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord)
- PNS – Peripheral Nervous System (cranial and spinal nerves)
- ANS – Autonomic Nervous System (sympathetic and parasympathetic).
CNS: Brain and Spinal cord.
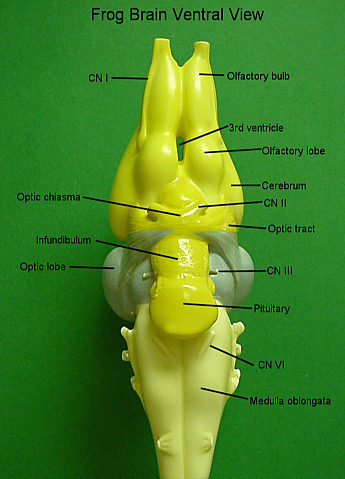
Brain
- Brain is situated in the cranial cavity.
- It is enclosed in a bony structure called brain box (cranium) and covered by two meninges (membranes) – piamater and duramater.
- There are 10 pairs of cranial nerves arising from the brain.
- The brain is divided into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain.

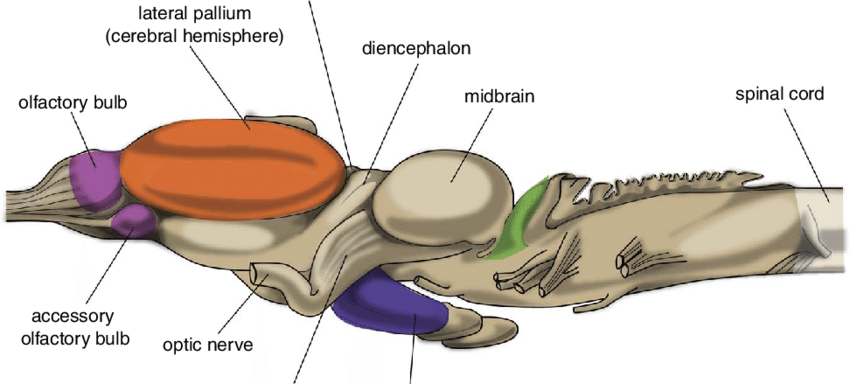
- Forebrain
- Fore brain (Prosencephalon) is the anterior most and largest part of the brain.
- It consists of a pair of olfactory lobes, paired cerebral hemispheres (as Telencephalon) and a diencephalon.
- Upper part of the olfactory lobes is narrow and free but is fused posteriorly.
- The olfactory lobes contain a small cavity called olfactory ventricle.
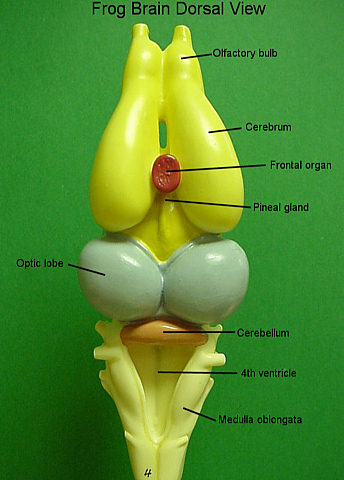
- Midbrain
- The midbrain is composed of a pair of optic lobes.
- Hindbrain
- Hind-brain consists of cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
- The medulla oblongata passes through a pore called foramen magnum and continues to form the spinal cord
- The spinal cord is enclosed in the vertebral column.
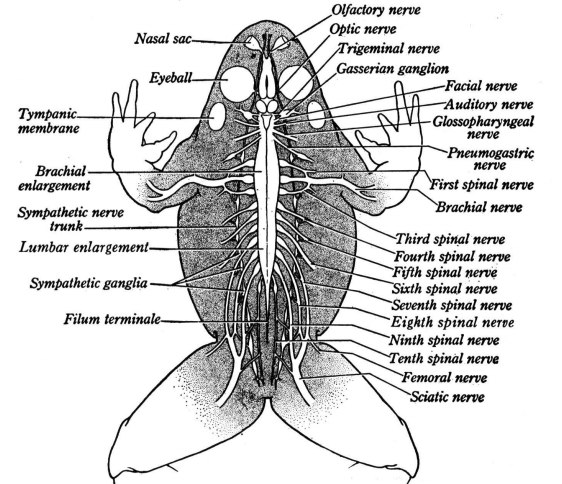
PNS: Cranial and Spinal nerves
Peripheral Nervous System consists of 10 pairs of cranial nerves and 10 pairs of spinal nerves.
ANS: Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Autonomic Nervous System is divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. They control involuntary functions of visceral organs
Sense organs
The sense organs of frogs are of two types.
Cell aggregates
These are sense organs composed of sensory cell aggregations around nerve endings.
- Sensory papillae – organs of touch
- Taste buds – organs of taste
- Nasal epithelium – Organs of smell
Well developed organs
- Eyes – organs of vision
- Tympanum – organs of hearing

Eyes
- Frogs have a pair of large eyes.
- They are situated in the orbit in skull.
- These are simple eyes (possessing only one unit).
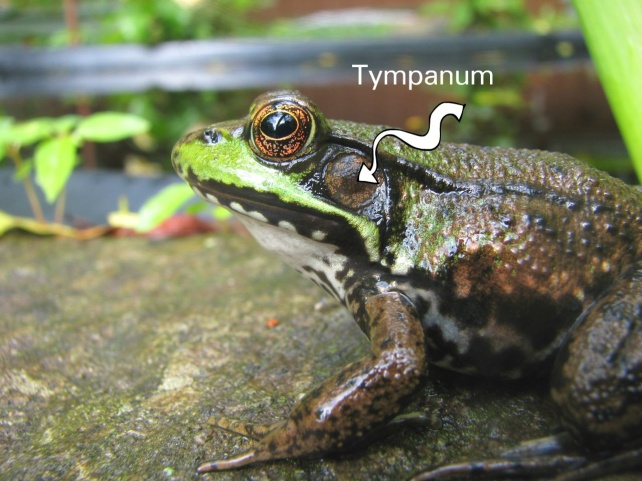
Tympanum
- External ear (pinna) is absent in frogs and only tympanum can be seen externally.
- The tympanum forms the eardrum of the frog.
- The ear is an organ of hearing as well as balancing (equilibrium).