Frogs belong to Class Amphibia of Phylum Chordata.The most common frog species found in India is Euphlyctis hexadactylus (formerly known as Rana tigrina).

Habitat
- Frogs can live both on land and in water. Some they mainly feed on insects. Some species also live on trees. Most of them are carnivorous.
- Frogs are poikilotherms or cold-blooded organisms. They do not have constant body temperature i.e. their body temperature varies with the temperature of the environment.
- Some species have the ability to change the colour to hide them from their enemies (camouflage). This protective coloration is called mimicry.

- During extreme climatic conditions, frogs take shelter in deep burrows to protect them from the heat and cold. This is known as summer sleep (aestivation) and winter sleep (hibernation) respectively.
Morphology
External Appearance
- The skin is smooth and moist due to the presence of mucus.
- The frog never drinks water but absorb it through the skin.
- The body of a frog is divisible into head and trunk, while the tadpole larva has a tail also.
- The dorsal surface of the body is greenish yellow with dark irregular spots. The ventral surface is pale yellow in color.
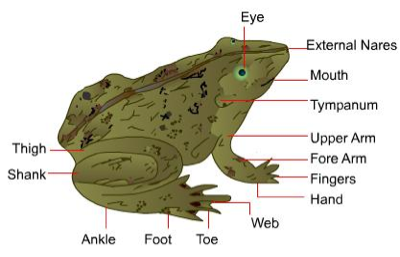
- Head
- The head is triangular. The snout is pointed.
- Mouth is present at the anterior end.
- A pair of nostrils is present above the mouth. It leads to buccal-pharyngeal cavity.
- Eyes
- The eyes are found behind the nostrils.
- Each eye is protected by an immovable upper and lower eyelid.
- The lower eyelid is further extended to form a thin transparent protecting sheath called nictitating membrane. It is water-proof and protects the eyeballs while the animal is in water.
- Ear
- Beneath each eye, there is a circular patch of skin which represents the ear. It is called tympanic membrane (tympanum) or eardrum.
- It receives sound signals.
- External ear (pinna) is absent.
- Trunk
- The trunk is broad and flat.
- There is small hump on the posterior dorsal side.
- The trunk bears a pair of short forelimbs and a pair of long hindlimbs.
- The posterior end of the trunk has an opening called cloaca, which is the common exterior opening of excretory and reproductive system.
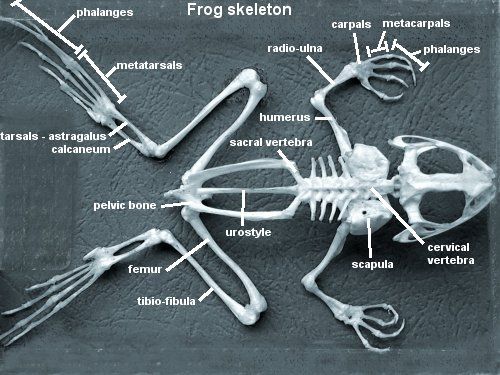
- Limbs
- The forelimbs have 3 parts – upper arm (brachium), forearm (antebrachium) and hand (manus). Only 4 digits are present on the forelimb.
- The hind limb is divided into – thigh (femur), shank (crus) and foot (pes).
- Foot has 5 webbed digits that aids in swimming.
- The limbs help in swimming, walking, leaping and burrowing.