The phenomenon in which more than one compounds have the same chemical formula but different chemical structures is known as Isomerism. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulae but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers. Compounds exhibiting this phenomenon of isomerism are known as isomers.
Geometrical Isomerism
- Its as we all know as cis- trans isomerism.
- There are different spatial arrangements of atoms in three-dimensional space in these isomers.
Doubly bonded carbon atoms have to satisfy the remaining two valences by joining with two atoms or groups. If these two atoms or groups which are attached to each carbon atom are different, they can be represented by YX C = C XY like structure. YX C = C XY can be represented in space in the following two ways :
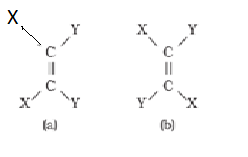
In (a), the two identical atoms i.e., both the X or both the Y lie on the same side of the double bond but in (b) the two X or two Y lie across the double bond or on the opposite sides of the double bond. This shows that disposition of atoms or groups in space in the two arrangements is different i.e. they have different geometry. Therefore, they are stereoisomers. If atoms or groups around C=C bond are to be rotatedthey would have the same geometry. But rotation around C=C bond is restricted and not free.
In order to understand this concept, take two pieces of strong cardboards and join them with the help of two nails. Holding one cardboard in your one hand, try to rotate the other. This way you can’t really rotate the other cardboard. The rotation is restricted. This illustrates that the restricted rotation of atoms or groups around the doubly bonded carbon atoms gives rise to different geometries of such compounds. The stereoisomers of this type are called geometrical isomers.
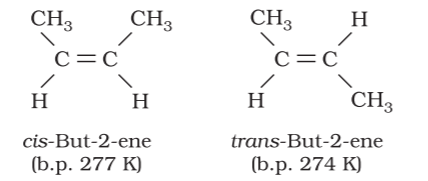
The isomer of the type (a) in which two identical atoms or groups lie on the same side of the double bond is called cis isomer and the other isomer of the type (b), in which identical atoms or groups lie on the opposite sides of the double bond is called trans isomer. This shows that cis and trans isomers have the same structure but have different configuration (arrangement of atoms or groups in space). These isomers differ in their properties like melting point, boiling point, dipole moment, solubility etc., due to this different arrangement of atoms or groups in space. Geometrical isomers of but-2-ene are shown below:
Polarity of Cis form of alkene is found to be more than the trans form. For example, dipole moment of cis-but-2-ene is 0.33 Debye, whereas, dipole moment of the trans form is almost zero or it can be said thattrans-but-2-ene is non-polar. By drawing geometries of the two forms as given below it becomes clear that in the trans-but-2-ene, the two methyl groups are in opposite directions, Therefore, dipole moments of C-CH3 bonds cancel, thus making the trans form non-polar.
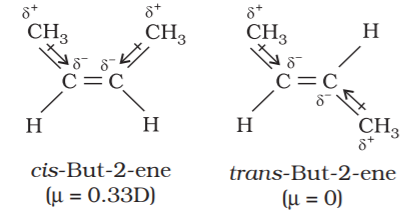
It is observed that the trans isomer has higher melting point than the cis form in case of solids. Geometrical or cis-trans isomerism is also shown by alkenes of the types XYC = CXZ and XYC = CZW.