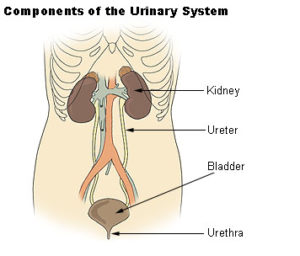
The human excretory system is used in the removal of waste products from the body. It comprises of the following:
- Two kidneys
- Two ureters
- One urethra
- One urinary bladder
Kidneys.
Kidneys are the main organs of the human excretory system and are paired in each individual with each one of them located on either side of the spine at the level of the liver. The functional unit of the kidney is called as the nephron. Kidneys are divided into:
- The renal cortex- the outer layer of the kidneys.
- The renal medulla- the inner layer.
- The renal pelvis- used to transport urine from the kidneys to the ureter.
Ureters.
As an extension of the renal pelvis, there is one ureter coming out of each kidney. The ureter is a thin muscular tube used to carry urine from kidneys to the bladder.
Urinary bladder.
The part of the kidney used in the storage of urine until its excretion from the body is the urinary bladder. It is shaped like an air sac structure lined with a smooth layer of muscle. Micturition is an act of urine removal from the body.
Urethra.
Through micturition, urine is expelled to the outside through urethra, a tube arising from the urinary bladder. It is longer in males and shorter in women. In males, it has another function of passing sperms into the vagina. It is usually guarded by a sphincter that is controlled automatically.
Structure of the Nephron.
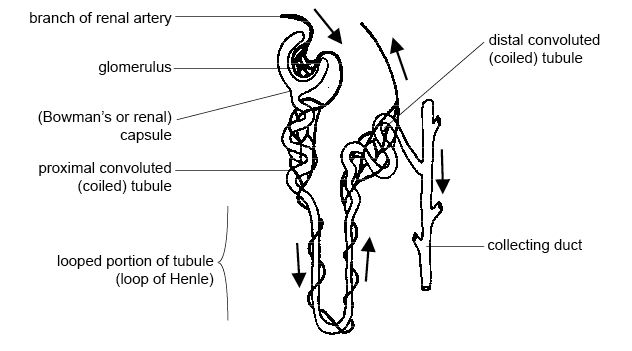
There are millions of nephrons in the kidneys that work together to filter urine and expel waste materials. Each kidneys is made up of the following parts:
- Bowman’s capsule.
Being the first part of the nephron, it receives the blood vessels. In this cup-shaped structure, glomerular filtration happens where proteins and blood cells remain in the blood.
- Proximal convoluted tubule.
It is formed by the extension of the Bowman’s capsule. It reabsorbs reusable materials and water from the blood.
- The loop of Henle.
It is a U-shaped structure formed from the extension of the proximal convoluted tubule. It is divided into three parts; the u-shaped bend, descending limb, and ascending limb. As water is being absorbed, urine becomes concentrated in this area. The descending limb is permeable to water, unlike the ascending limb which is impermeable to it.
- Distal convoluted tubule.
The loop of Henle leads to this structure. This is where the effect of kidney hormones is felt. It further leads to the collecting ducts.
- Collecting duct.
Each nephron’s distal convoluted tube leads to the collecting ducts. They together form the renal pelvis used for passage of urine into the ureter and further into the urinary bladder.
Other excretory organs.
- Skin: Being the largest organ in the body, it assists in excretion by way of sweating, which eliminates sodium chloride and some of the urea.
- Lungs: The primary parts of the respiratory system, they help in the intake of oxygen and expulsion of carbon dioxide.
- Liver: Compounds such as fats, hormones, and alcohol are defended against the body by the liver. The first metabolism of drugs occurs in the liver. It also plays a bigger part in the elimination of excess fats and cholesterol.