Human insulin was the initially recombinant bio-pharmaceutical approved in the US in 1982. Before that it introduction, protein products approved for use in humans were drawn from natural sources. Thus the discovery of new bio-pharmaceutical started at a rather leisurely pace. The hormone insulin is essential for the control of blood sugar ranges. Diabetes mellitus is a disease that some people cannot make insulin themselves. This disease is killing many people in the world every year.
Production of Genetic Engineered Insulin
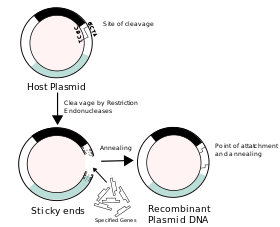
- This human insulin is extracted from pancreas cells and an insulin-producing gene is isolated.
- A plasmid DNA is drawn from a bacterium and cut with a restriction enzyme, forming plasmid vector.
- Put human insulin-producing gene into the bacterial plasmid vector to produce the recombinant DNA of the human insulin-producing gene.
- This recombinant DNA is introduced into a bacterial cell to form the recombinant bacterium.
- The recombinant bacteria increase in a fermentation tank and produce human insulin.
- Insulin is drawn, purified and bottled. It is then it is to be injected into diabetic patients.
Recombinant HB Vaccine Production
- Hepatitis B saw as one of the most common infectious diseases known to man.
- It is concluded by the World Health Organization that there are as many as 285 million chronic carriers of this virus worldwide.
- Traditional vaccines make use of a weakened or killed form of a virus to force the body to develop antibodies which are strong enough to battle the virus.
One of the Traditional Vaccination for Hepatitis B
Recombivax HB
Recombivax HB as one of the known traditional vaccination for Hepatitis B was approved as a hepatitis B prevention vaccine in July 1986. Using recombinant DNA technology, Recombivax HB makes use of the surface antigen of the virus which stimulates the production of protective antibodies that battle the HB virus.
Recombivax HB Production
- HB antigen producing gene is quarantine from the HB virus.
- A plasmid DNA is drawn from a bacterium and is cut with a restriction enzyme to form the plasmid vector.
- The isolated HB antigen producing gene is put into the bacterial plasmid vector to form the recombinant DNA.
- This recombinant DNA, containing the target gene, is introduced into a yeast cell to form the recombinant yeast cell.
- The recombinant yeast cell multiplies in the fermentation tank then produces the HB antigens.
- The HB antigens are drawn, purified and bottled. It is ready for vaccination in humans.