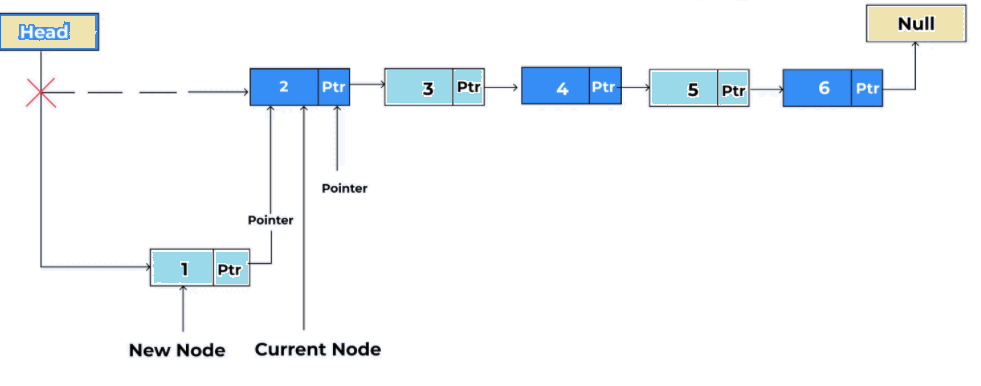
We just need to make a few adjustments in the node links to insert a new element into a singly linked list at the beginning. This process involves the below steps:
- Use the below statements to allocate the space for the new node. It also stores the data into the data part of the node.
ptr = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node *)); ptr → data = item
- Use the below statement to make the linked part of the new node pointing to the existing first node of the list.
ptr->next = head;
- Use the below statement to make the new node as the first node of the list.
head = ptr;
Algorithm
- Step 1: IF pointer = NULL Then Go to step 7 that is exit otherwise follow step2 [END OF IF]
- Step 2: SET New_Node = pointer
- Step 3: SET pointer = pointer → next
- Step 4: SET New_Node → data= value
- Step 5: SET New_Node →next =head
- Step 6: SET head = New_Node
- Step 7: Exit
C Example:
#include #include void beginInsert(int); struct node { int data; struct node *next; }; struct node *head; void main () { int choice,element; do { printf("\nEnter the element to insert:\n"); scanf("%d",&element); beginInsert(element); printf("\nPress 0 to insert more elements.\n"); scanf("%d",&choice); }while(choice == 0); } void beginInsert(int element) { struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node *)); if(ptr == NULL) { printf("\nOVERFLOW - Exit\n"); } else { ptr->data = element; ptr->next = head; head = ptr; printf("\nNode successfully inserted.\n"); } } |
Output
Enter the element to insert: 2 Node successfully inserted. Press 0 to insert more elements. 0 Enter the element to insert: 4 Node successfully inserted. Press 0 to insert more elements.