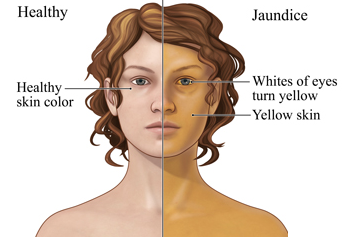
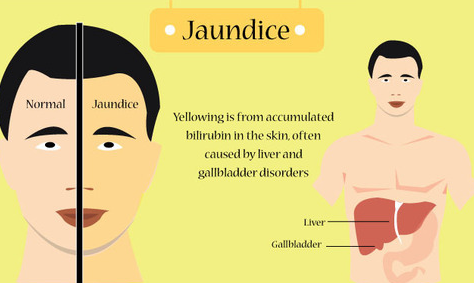
Jaundice could be a yellow discoloration of the skin, mucose membranes, and also the whites of the eyes caused by increased amounts of haematoidin within the blood. Jaundice may be a sign of an underlying illness method. Bilirubin is a by-product of the daily natural breakdown and destruction of red blood cells within the body. The hemoprotein molecule that’s free into the blood by this method is split, with the hematin portion undergoing a chemical conversion to haematoidin.
Normally, the liver metabolizes and excretes the bilirubin within the variety of gall. However, if there’s an interruption during this usual metabolism or production of haematoidin, jaundice might result.
Causes
Jaundice could also be caused by many different illness processes. It is useful to grasp the various causes of jaundice by distinguishing the issues that disrupt conventional bilirubin metabolism and/or excretion.
-Pre-hepatic (before bile is made in the liver)
Jaundice within these cases is usually a result of a fast increase in the breakdown and destruction of the red blood cells (hemolysis), overwhelming the liver’s ability to properly take away the increased levels of bilirubin from the blood.
-Hepatic (the problem arises within the liver)
Liver’s inability to properly metabolize and discharge haematoidin.
-Post-hepatic (after bile has been made in the liver)
Newborn jaundice
Jaundice in newborn babies will be caused by many different conditions, though it’s usually a standard physiological consequence of the newborn’s immature liver. Even though it’s sometimes harmless underneath these conditions, newborns with extremely elevated levels of bilirubin from other medical conditions may suffer serious brain damage if the root cause is not addressed.
Common causes of newborn jaundice:
-Physiological jaundice
It’sevident on the second or third day of life. It is the foremost common reason for newborn jaundice and is sometimes a transient and harmless condition.
-Maternal-fetal blood group incompatibility (Rh, ABO)
Incompatibility between the blood varieties of the mother and also the foetus.
-Breast milk jaundice
It happens in breastfed newborns and frequently seems at the tip of the primary week of life.
-Breastfeeding jaundice
If the breastfed newborn doesn’t receive adequate breast milk intake.
-Cephalohematoma (a collection of blood under the scalp)
Sometimes throughout the parturition process, the newborn might sustain a bruise or injury to the top, leading to a blood collection/blood clot underneath the scalp.
Common signs and symptoms
-Yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes,
-Light-colored stools,
-Dark-colored urine, and
-Itching of the skin.
-Nausea and vomiting,
-Abdominal pain,
-Fever,
-Weakness,
-Loss of appetite,
-Headache,
-Confusion,
-Swelling of the legs and abdomen,
Newborn jaundice
In newborns, as the bilirubin level increases, jaundice will progress from the head to the -abdomen, and from there to the hands and feet. Additional signs and symptoms that will be seen within the newborn include:
-Poor feeding,
-Lethargy,
-Changes in muscle tone,
-High-pitched crying, andseizures.
Treatment
-Treatment might accommodates expectant management (watchful waiting) reception with rest.
-Medical treatment with intravenous fluids, medications, antibiotics, or blood transfusions may be required.
-If a drug/toxin is that the cause, these must be discontinued.
-In sure cases of newborn jaundice, exposing the baby to special colored lights (phototherapy) or exchange blood transfusions could also be needed to decrease elevated bilirubin levels.