String handling is a way of handling and manipulating strings in java with the help of a lot of concepts like concatenation, comparison, etc.
String:
- In General – A string is a sequence of characters.
- In Java – A string is an object which is created by using the String class. String objects are immutable and they can’t modified i.e. any change in the existing object will result in a new object.
How to create a string object?
- By String literal.
- By new keyword.
1. By String literal:
String literal: A sequence of characters enclosed in double-quotes. String literal is a concept of Java language. It is not an object from java.lang.String. e.g. – “Hello java”. In the string literal case, one object and one reference variable are created. The object is placed in a string-constant pool.
String literal/constant pool: is a special part of heap memory used to store string literals or string constants.
Every time a literal is created, JVM checks the string constant pool for it. If the string literal is already in the pool then no new object will be created in the pool, a reference of the already existing object will return. If a string literal is not exist in the string constant pool then a new instance will be created and placed in the string constant pool.
E.g. –
String str1 = “w3schools” String str2 = “w3schools”
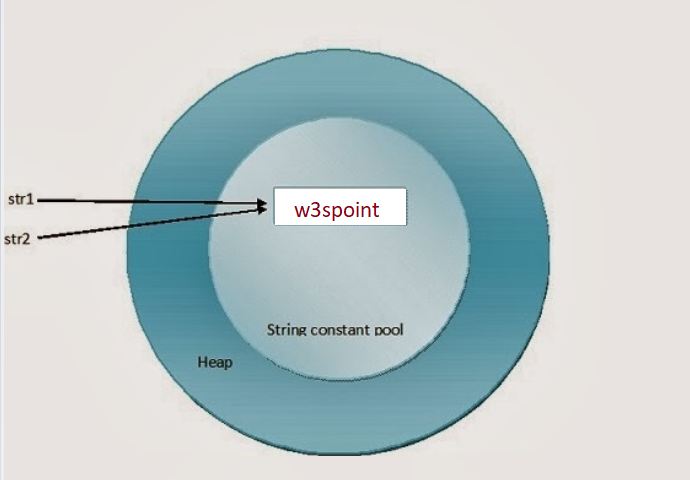
In the above example in the case of str1 JVM checks for “w3schools” in the string constant pool. The first time it will be not in the pool hence JVM creates a new instance and places it into the pool. In the case of str2, JVM will find the “w3schools” in the pool. Hence no new instance will be created and reference of the already existing instance will be returned.
Java uses the concept of Java literal to increase memory efficiency. No new instance will be created for a string literal if it already exists in the string constant pool.
2. By new keyword:
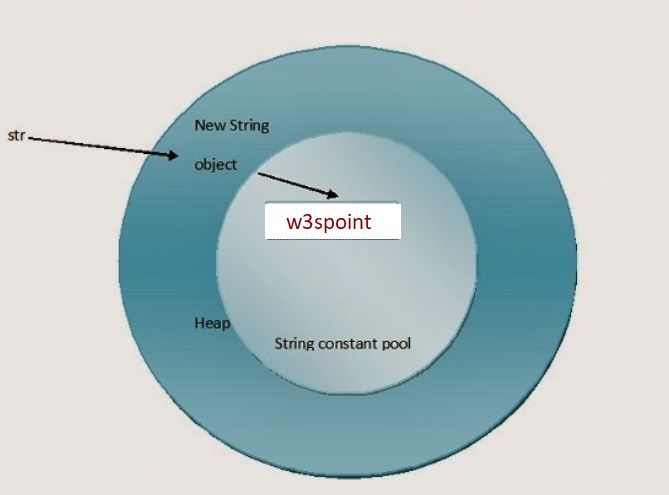
String objects can be created with new keywords also. In this case, two objects and one reference variable are created. One object is created in the heap area (non-pool) and the other (string literal) is placed in the string constant pool. The variable will refer to the object in the heap area.
e.g.- String str = new String(“w3schools”).
Why string objects are immutable in Java?
As we discussed above java uses the concept of String literal. Suppose n reference variables refer to one object “w3schools”. If one reference variable changes the value of the object, it will be affected by all other n-1 reference variables. That’s why string objects are immutable in Java.