Annotations for Junit testing:
1. @Test: It is used to specify the test method.
2. @BeforeClass: It is used to specify that method will be called only once, before starting all the test cases.
3. @AfterClass: It is used to specify that method will be called only once, after finishing all the test cases.
4. @Before: It is used to specify that method will be called before each test case.
5. @After: It is used to specify that method will be called after each test case.
6. @Ignore: It is used to ignore the test case.
Example:
DivisionTestCase.java
import org.junit.After; import org.junit.AfterClass; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.BeforeClass; import org.junit.Ignore; import org.junit.Test; /** * This is test case class for basic JUnit annotation use. * @author w3schools */ public class DivisionTestCase { //called only once, before starting all the test cases. @BeforeClass public static void beforeClass() { System.out.println("In beforeClass method."); } //called only once, after finishing all the test cases. @AfterClass public static void afterClass() { System.out.println("In afterClass method"); } //called before each test case. @Before public void before() { System.out.println("In before method"); } //called after each test case. @After public void after() { System.out.println("In after method"); } //define the test case. @Test public void testCase1() { System.out.println("In testCase1"); } //define the test case. @Test public void testCase2() { System.out.println("In testCase2"); } //ignore the test case.It will not execute. @Ignore @Test public void testCase3() { System.out.println("In testCase3"); } } |
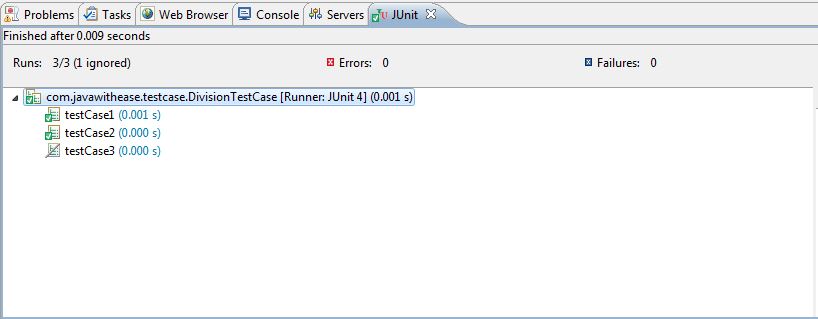
Output:
In beforeClass method.
In before method
In testCase1
In after method
In before method
In testCase2
In after method
In afterClass method |
Download this example.
Next Topic: JUnit expected exception test.
Previous Topic: JUnit framework.