- Lipids are a heterogeneous group of organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen and a few atoms of oxygen.
- The term lipid is derived from greek word lipos, meaning fat.
- These substances are not soluble in water but dissolve in non-polar solvents such as benzene, ether, chloroform. This is because they contain long hydrocarbon chains that are non-polar and thus hydrophobic.
- The main groups of compounds classified as lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids and waxes.
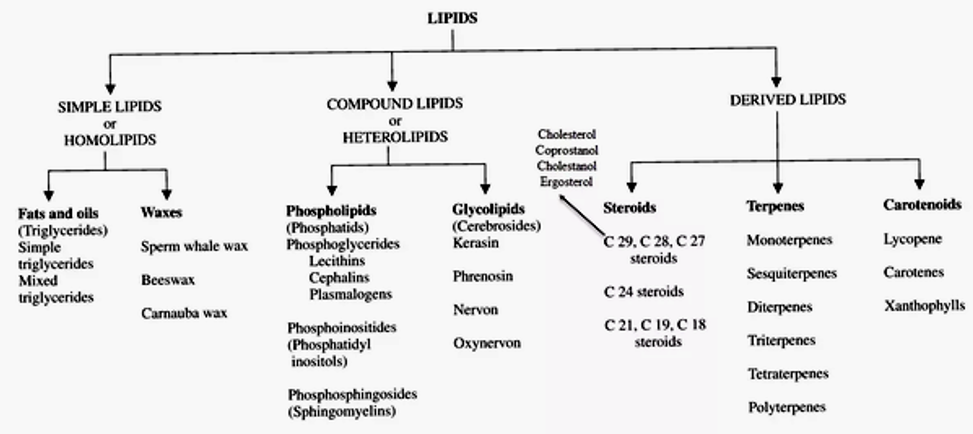
(i) Oils
- They are esters of fatty acids with glycerol and are liquids at room temperature.
- They are rich in unsaturated fatty acids.
- They have a low melting point.
- They are more reactive and easily digestible than fats, hence doctors advise intake of oils more than fats.
e.g. Mustard oil, sunflower oil, rape seed oil, sesame oil.
(ii) Fats
- They are esters of fatty acids with glycerol and are solids at room temperature
- They are rich in saturated fatty acids.
- They have a high melting point.
- They are less reactive and gets deposited in the blood vessels, hence doctors advice not to include more of these in our diet
e.g., Butter, Ghee, Vanaspati.
(iii) Waxes
- They are esters of fatty acids with a long chain alcohol, but not glycerol.
- They form water insoluble coatings on hair and skin of animals and on leaves, stems and fruits of plants and provide protection.
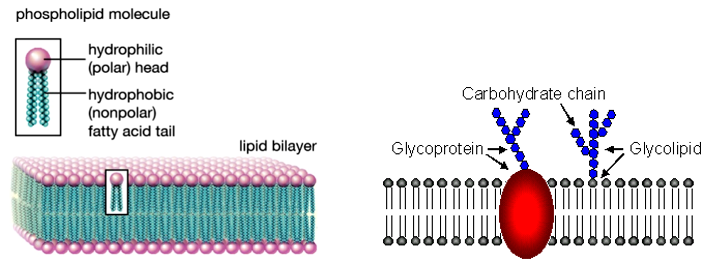
(iv) Phospholipids
- They are compound lipids and have a phosphate group along with fatty acids and alcohol (glycerol).
- It serves as major structural component of cell membrane
- These lipids have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.
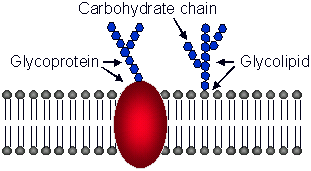
(v) Glycolipids
- They have one or more sugars (carbohydrates) along with the fatty acids and alcohol (glycerol).
e.g., Cerebrosides (white matter) and Gangliosides (grey matter).
(vi) Sphingolipids
- They have amino-alcohols in their molecules instead of glycerol e.g., sphingomyelin in brain cells.
(vii) Sterol
- Cholesterol is the sterol alcohol present in animal cells either free or as esters.
- It is a precursor of steroid hormones like progesterone, estradiol, cortisol and testosterone
- Diosgenin, a steroid compound from Dioscorea (yam) is used to manufacture antifertility pills.
Functions of Lipids
- Lipids provide energy and they are the reserve form of energy
- Fats act as insulators and protect the body from heat loss.
- Phospholipids form an important part of all biomembranes in cells.
- Cholesterol is the precursor of steroid hormones, vitamin D and bile salts.
- Lipids form the white matter, grey matter of brain and myelin sheath of nerves.