List, Set, and Map interfaces are very important part of collection framework. List and Set implements Collection interface but Map does not. Let us discuss all with examples and differences.
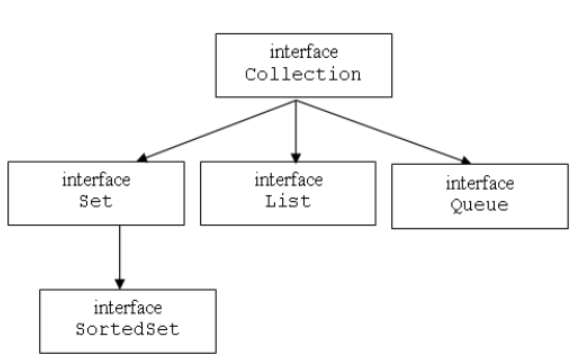
Collection Hierarchy:
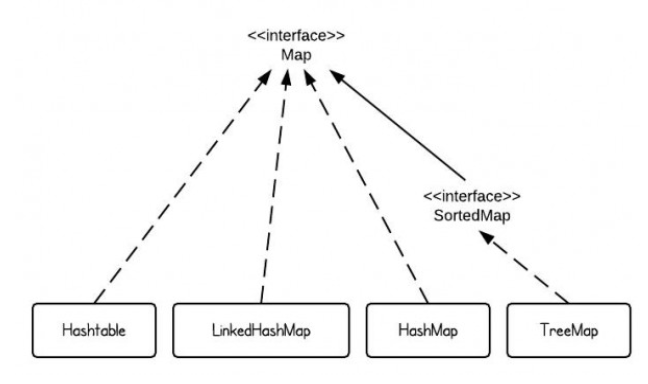
Map Hierarchy:
List
A List in java extends the collection interface and represent an sequenced or ordered group of elements. It can contain duplicate elements. It also defines some additional methods which it inherits from Collection interface.
Note: Elements in List can be inserted, updated, or retrieved by their position or index. Index or position value starts from 0.
Example
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ //Create List object List<String> mySubjects = new ArrayList<>(); //Add elements to list mySubjects.add("Java"); mySubjects.add("Spring"); mySubjects.add("Hibernate"); //Add elements at specified position mySubjects.add(1,"SQL"); mySubjects.add(2,"Oracle"); System.out.println("My Subjects:"); //Print all subjects for(String subject : mySubjects){ System.out.println(subject); } //Print element on 2nd index System.out.println("Element at 2nd index: "+mySubjects.get(2)); } } |
Output
My Subjects: Java SQL Oracle Spring Hibernate Element at 2nd index: Oracle |
Set
A set represents a group or collection of items. Set has a special property that is unique items, it can not contain a duplicate item or element. It extends the collection interface.
Note: Set interface does not have any additional method other than methods inherited from Collection interface. With all collection interface methods it adds the restriction that it can not contain a duplicate elements.
Example
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ //Create Set object Set<String> mySubjects = new HashSet<>(); //Add elements to Set mySubjects.add("Java"); mySubjects.add("Spring"); mySubjects.add("Hibernate"); System.out.println("My Subjects:"); //Print all subjects for(String subject : mySubjects){ System.out.println(subject); } } } |
Output
My Subjects:
Java
Hibernate
Spring |
Map
A map in java, not extends the Collection interface. It represents a group of special elements or objects. Every map element or object contains key and value pair. A map can’t contain duplicate keys and one key can refer to at most one value.
Example
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ Map<Integer,String> mysubjects = new HashMap<Integer,String>(); //Add elements to map mysubjects.put(1,"Java"); mysubjects.put(2,"Spring"); mysubjects.put(3,"Oracle"); //Print map elements in key value form for(Map.Entry subject : mysubjects.entrySet()) System.out.println(subject.getKey()+" - "+subject.getValue()); } } |
Output
1 - Java 2 - Spring 3 - Oracle |
When to use List, Set and Map in Java?
Use of a data structure or collection is depends upon the requirement.
- Use Set: If you need group of unique elements.
- Use List: If get operations are higher than any other operation.
- Use Map: If objects contains the key and value pair.
Difference between List, Set, and Map
| List | Set | Map |
| Allow duplicate elements. | Does not allow duplicate elements. | Does not allow duplicate key but values can be duplicate. |
| Allow multiple null values. | Allow single null value. | Allow single null as key and multiple null as values. |
| Maintains insertions order. | Set represents an unordered collection but some of its implementation classes maintains some order. LinkedHashSet maintains order, TreeSet maintains ascending order. | Like Set, Map also represents an unordered collection. Again same like Set, some of its implementation classes maintains some order. TreeMap maintains ascending order of keys. |
Java interview questions on collections
- What is the difference between arraylist and vector in java?
- What is the difference between arraylist and linkedlist?
- What is the difference between Iterator and ListIterator?
- What is the difference between Iterator and Enumeration?
- what is the difference between list and set in java?
- what is the difference between set and map in java?
- what is the difference between hashset and treeset in java?
- what is the difference between hashset and hashmap in java?
- what is the difference between hashmap and treemap in java?
- what is the difference between hashmap and hashtable in java?
- what is the difference between collection and collections in java?
- what is the difference between comparable and comparator interfaces?
- what is the hashcode method in java?
- Java equals method
- Java hashCode method
- Why to override hashcode and equals method in java?
- How hashmap works intrnally?
- How put and get works in hashmap?
- How to resolve collision in hashmap?
- How hashmap stores null key?
- How hashset works intrnally?