Lysosomes are tiny bags filled with digestive enzymes concerned with intracellular digestion. These are the recently discovered organelles of the cell. It occurs in most animal cells and in a few plant cells.
- It is a lytic body. It destroys the cell in which it is produced. So it is called suicidal bag.
- As the lysosome digests the components of the cells, it is often referred to as the digestive tract of the cell.
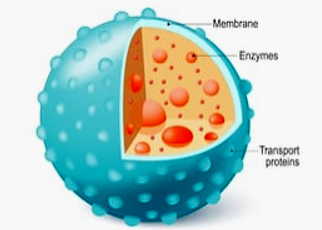
- They are usually spherical in shape, filled with dense granules having a variety of hydrolytic enzymes. When the membrane is punctured the enzymes are released and become active.
- The lysosomal enzymes are collectively called hydrolases. It cleaves: the substrate by the addition of a water molecule (hydrolysis).
- The hydrolases present in lysosomes are – lipases, proteases, carbohydrases and nucleaases. These enzymes are capable of digesting lipids, proteins carbohydrates and nucleic acids respectively.
- They areoptimally active at the acidic pH.
Functions
- It digests foreign materials.
- It digests food,materials.
- It brings about chromosomal breakages.
- During fertilization the egg membranes dissolve by the action of lysosomes, which make way for the entry of sperm into the egg
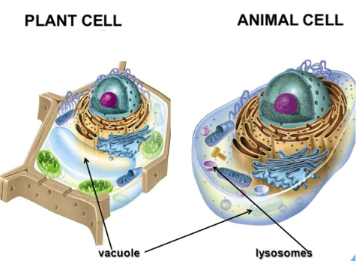
- Usually lysosomes are absent in plant cells. But plant cells contain membrane bounded vesicles containing enzymes called Spherosomes
Vacuoles
These are membrane bound fluid filled or hollow cytoplasmic structures; which are found in all plant cells and animal cells such as protozoa, adipose tissue etc.
Frey Wyssling and Muhlethalas have reported the origin of vacuoles from the invagination of the plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum. These small vacuoles are called provacuoles. Many pro vacuoles fuse together to form a large vacuole
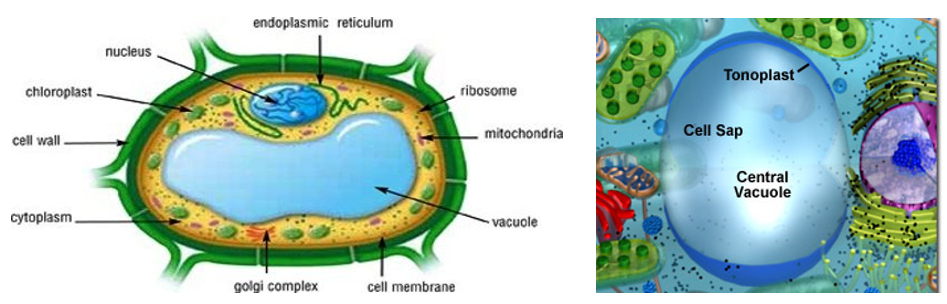
Structure
- They are spherical or oval in shape.
- The vacuole is bound by a single lipoproteinaceous unit membrane called tonoplast.
- In plants, the tonoplast facilitates the transport of a number of ions and other materials against concentration gradients into the vacuole; hence their concentration is significantly higher in the vacuole than in the cytoplasm.
Composition
- It usually contains water, sap, excretory product and other materials not useful for the cell.
- In plant cells the vacuoles can occupy up to 90 per cent of the volume of the cell.
- They are filled with water, phenol, flavonoids anthocyanin, alkaloids and storage products such as sugar and proteins.
Functions
- They serve as a storage bag.
- They are involved in material transport within the cytoplasm.
- They maintain internal pressure of the cell.
- In Amoeba the contractile vacuole is important for osmoregulation and excretion.
- In many cells, as in protists, food vacuoles are formed by engulfing the food particles
- The water content of the vacuole is responsible for the turgidity of the plant cells