The reproductive system is essential for the production of new living orgasm. The ability of procreation is a basic characteristic of life.
Two individuals produce a progeny or offspring that have genes from both parents.
The reproductive system is consistent of both male and female reproductive organs and structures which are regulated by hormones.
Reproductive organs are usually considered to be primary or secondary organs.
Male
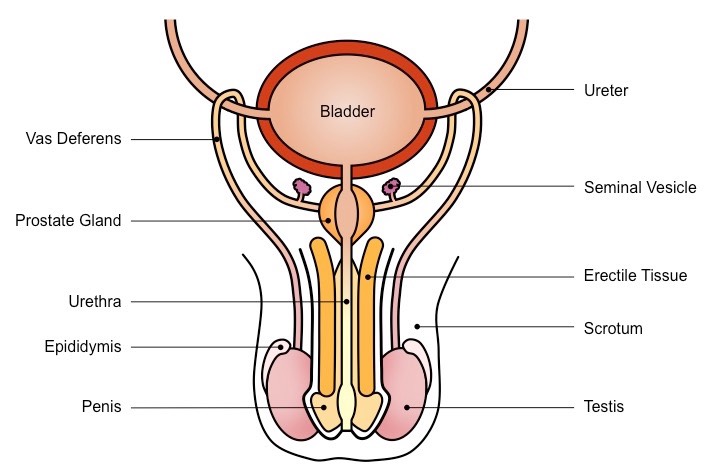
Male reproductive system consists of accessory glands, and a series of duct system that provide a pathway for fertile sperm cells to exit the body.
1-Testis produce sperm and testosterone.
2-Epididymis helps in maturing and storing sperm.
3-Sperm duct carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
4-Seminal vesicles, Cowper’s gland and Prostrate gland produces seminal fluid which feeds the sperm and allows them to swim. Sperm and seminal fluids are collectively called semen.
5-Urethra allows the passage of either urine or sperm. Sphincters intercepts urine from entering the urethra while semen is passing through.
6-Penis places sperm inside the body of a female
7-Scrotum keeps testis at a temperature level. This is the optimum temperature for Meiosis occur.
Female
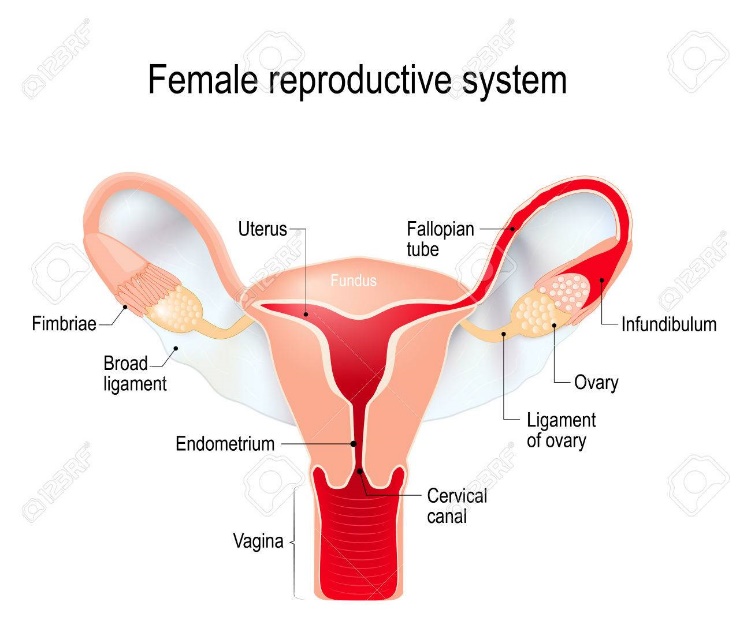
Equivalently, the female reproductive system contains organs and structures that promote the production, support, growth, and development of female gametes (egg cells) and a growing fetus.
1-Ovaries produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone site of ovum (egg cell) development and ovulation. Primary reproductive structures that create gametes and sex hormones. There’s one ovary on both sides of the uterus.
2-Fallopian tubes (oviducts) carry the ovum from the ovary to the uterus, usually transport it to the site of fertilization.
3-Vagina fibrous, muscular canal extends from the cervix to the external environment, provides a passageway for sperm and menstrual flow also functions as birth canal.
4-Fimbrae sweep the ovum into the fallopian tube following ovulation.
5-Uterus (womb) pear-shaped organ in which the embryo and fetus develop, involved in menstruation. After fertilization, provides a place for baby to develop.
6-Cervix separates the vagina from the uterus, also holds the fetus in place during pregnancy and dilates during birth to allow the fetus to leave the uterus.
The construction of sperm cells is well known as spermatogenesis. This process take place continuously within the male testes. Hundreds of millions of sperm must be enabled in order for fertilization to take place.
Oogenesis (ovum development) takes place in the female ovaries. In meiosis I of oogenesis, daughter cells are sorted asymmetrically. These asymmetrical cytokinesis results in one massive egg cell (oocyte) and smaller cells known as polar bodies. The polar bodies deteriorate and are not fertilized. When meiosis is accomplished, the egg cell is called a subordinate oocyte. The haploid secondary oocyte will possibly complete the following meiotic stage if it come across a sperm cell, the fertilization begins. Once fertilization is established, the lower oocyte completes meiosis II and is then called an ovum. The ovum amalgamate with the sperm cell, and then the fertilization is complete. The inseminate ovum is called a zygote.