Mitochondria are thread like or granular cytoplasmic organelles (mito-thread, chondrion-granule). It was first observed by Flemming and Kolliker in 1882. The term mitochondria were introduced by Benda in 1898.
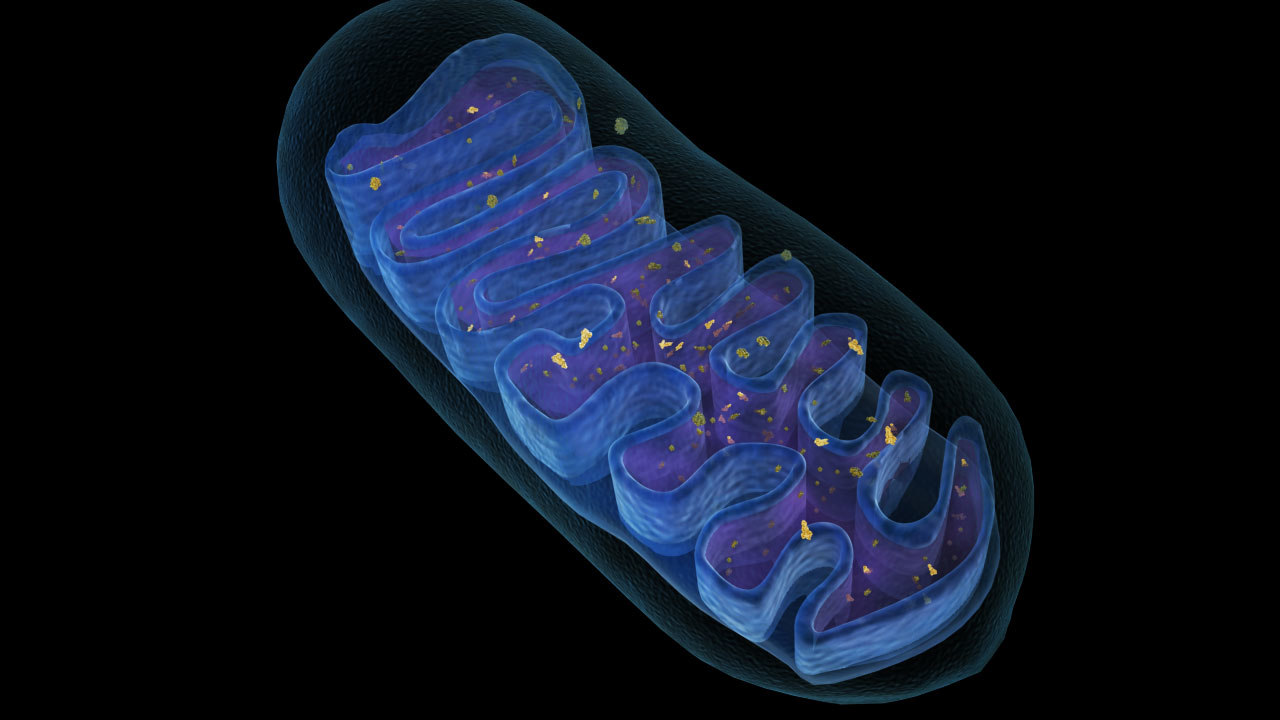
They are found both in plant and animal cells, but absent in prokaryotes.
The number of mitochondria is particularly related to the functional state of the cell. If the metabolic activity is high the number of mitochondria is also high.
Structure
- It may be filamentous or granular in shape, depending upon the physiological conditions of the cell.
- The mitochondria are covered by two unit membranes, namely outer and inner mitochondrial membranes, which are lipo-proteinaceous in nature.
- The two membranes are separated by a space called peri-mitochondrial space.
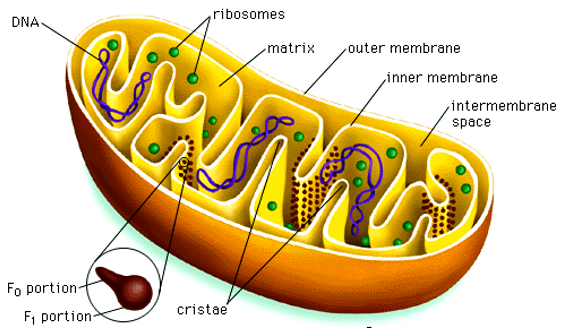
- The inner membrane encloses a space filled with a fluid called matrix.
- They contain proteins, lipids, ribosomes, RNA, DNA, respiratory enzymes etc.
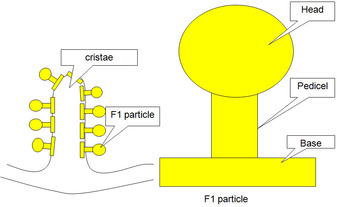
- The membrane gives out a number of finger – like projections known as cristae.
- The cristae and inner surface of inner membrane bear certain tennis-racket like small particles called elementary particles or oxysomes or F1 particles or Electron Transport Particles (ETP).
- These are the actual site of energy transfer or oxidative phosphorylation.
- Mitochondria contain one or more DNA called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA.
- It is circular and double stranded. It can self replicate and also produces RNA like that of nuclear DNA. Since they are able to replicate themselves due to the presence of DNA, they are called semi autonomous organelles.
Energy Site of the cell
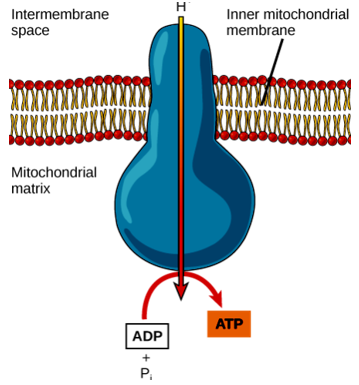
- Mitochondria are the energy sites of the cell.
- They synthesize and store the energy rich compound, ATP.
- When a site is in need of energy, mitochondria get collected around the site.
- The mitochondrial membrane contracts and squeezes out ATPs.
- Since they are the centers of production, storage and distribution of energy for various metabolic activities of the cell, mitochondria are said to be the powerhouse of the cell.
- The oxidation of glucose, fatty acids, amino acid etc. takes place in mitochondria
Functions
- It is the site of aerobic oxidation of glucose through the citric acid cycle and Electron transport system.
- Production of ATP, the energy currency of celI, through oxidative phosphorylation.
- Calcium accumulation
- Energy supply
- Cell respiration