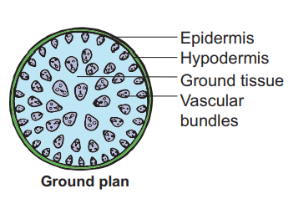
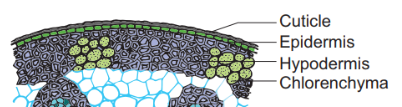
Epidermis:
- It is made up of a single layer of cells with an external coating of waxy cuticle.
- Epidermal outgrowths are usually absent.
- Very few stomata are found.
Hypodermis:
- It is composed a few layer of sclerenchyma cells lying just below the epidermis.
- It gives mechanical support to the stem.
Ground Tissue:
- The ground tissue is not differentiated into cortex, epidermis pericycle or pith.
- It is composed of a large mass of loosely arranged parenchyma cells found next to hypodermis.
- The cell wall is composed of cellulose.
- The cells contain reserve food materials.

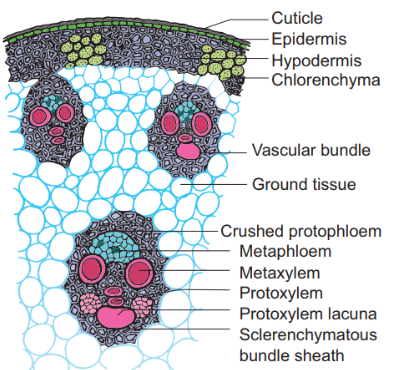
Vascular tissue
- The vascular bundles are embedded within the ground tissue.
- Numerous bundles are found scattered throughout the ground tissue.
- Smaller bundles are seen towards the periphery and are more crowded.
- The larger ones are seen towards the centre and are more spaced.
- Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath.
- The bundles are collateral closed. It is a characteristic feature of monocot stem.
| Dicot Stem | Monocot Stem |
| Epidermis – Have outgrowths (trichomes) | Epidermis – No outgrowths |
| Hypodermis – Made of collenchyma | Hypodermis – Made of sclerenchyma |
| Ground tissue – Differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericycle, medulllary rays and pith. | Ground tissue – No Differentiation |
| Xylem & Phloem – Few in number | Xylem & Phloem – Numerous |
| Vascular bundles – Arranged in the form of a brocken ring | Vascular bundles – Scattered in the ground tissue |
| Cambium – Present between the xylem and phloem | Cambium – Absent, hence closed type |
| Phloem parenchyma – Present | Phloem parenchyma – Absent |
| Vascular bundles – Have a sclerenchymatous bundle cap | Vascular bundles – Have a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath |