The nervous tissue is composed of densely packed nerve cells commonly known as neurons. The neurons are capable of conducting nerve impulses. The nervous tissue arises from ectoderm of a growing embryo.
Neurons
- There are more than 100 billion neurons in a nervous system.
- They vary in shape and size.
- All neurons have 3 main parts – a cell body, few dentrites, and an axon.
- The cell body contains a large nucleus and several other structures such as mitochondria, Lysosomes, Nissl bodies and neurofilaments, which are involved in the metabolism, growth and repair of the neuron.
- Dentrites are thread-like branched cytoplasmic extensions arising from the cell body. They are involved in the conduction of nerve impulses towards the cell body.
- Axon is a long unbranched cytoplasmic extension which conducts an impulse away from the cell body.
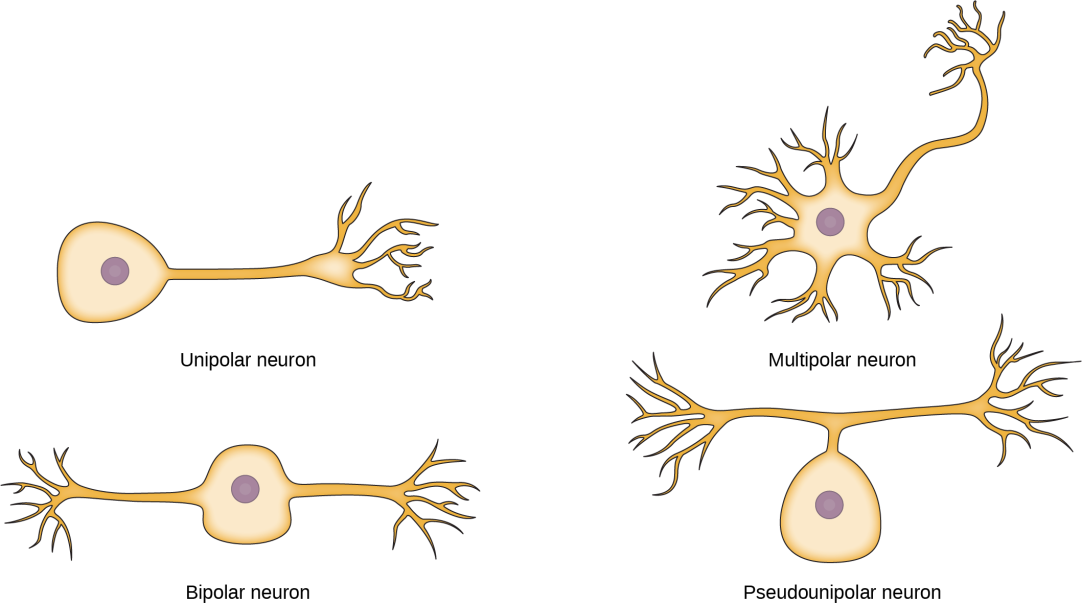
Based on the number of dentrites, the neurons are classified into 3 groups
- Unipolar
- Bipolar
- Multipolar
Neuroglial cells
- The rest of the nervous system is composed of non- conducting cells called neuroglial cells.
- These cells make up more than one-half of the volume of the total nervous system.
- Their main function is to protect, nurture and support the neurons.
- There are 4 types of neuroglial cells – Astrocytes, Oligodendrocytes, Microglial cells and Ependymal cells.
- Astrocytes: It is the largest and most abundant of all glial cells. These cells have long star-like processes. Astrocytes form the blood-brain barrier.
- Oligodendrocytes: They are small glial cells with several processes. They are found in the grey and white matter of CNS.
- Microglial cells: These are the smallest of all glial cells. They are either cuboidal or columnar cells. Functionally, macroglial cells are macrophages. They engulf damaged nerve cells.
- Ependymal cells: They are elongated cells found as a single layer in the lining of spinal cord and ventricle of the brain.
Nerve impulse conduction
When a neuron receives a stimulus, an electrical disturbance is created inside the cell, which travels along the cell plasma membrane. When the signal reaches nerve endings, it stimulates the nearby neurons.