WordPress – Permalink Setting
The URLs of the page you write on your WordPress website are known as permalinks. Permalinks are what visitors enter into their browser URL bar to view one webpage of your website (they are the permanent connection to a single page). They are also what search engines and other websites use to connect to your WordPress site. Due to this, they are very significant.
You can customize the structure of your permalinks at any time. However, making this will modify the URL of your pages. This can generate your search engine traffic and referral traffic to drop considerably as visitors are given with 404-page errors instead of the page they desire to view.
301 redirects can prevent the impact of a shift in permalink structure. However, it is still better to configure your website with the permalink structure you need from the beginning.
There are a few choices for what permalink structures WordPress has available, and each of them has its own advantages. No matter what, having clean URLs on your website is very valuable.
The Default Permalink Structure
WordPress permalink settings can be seen in the main settings menu of the WordPress admin section (i.e. https://example.com/wp-admin/options-permalink.php).
In the screenshot below, you can notice the five types of permalink structures that WordPress displays as common settings.
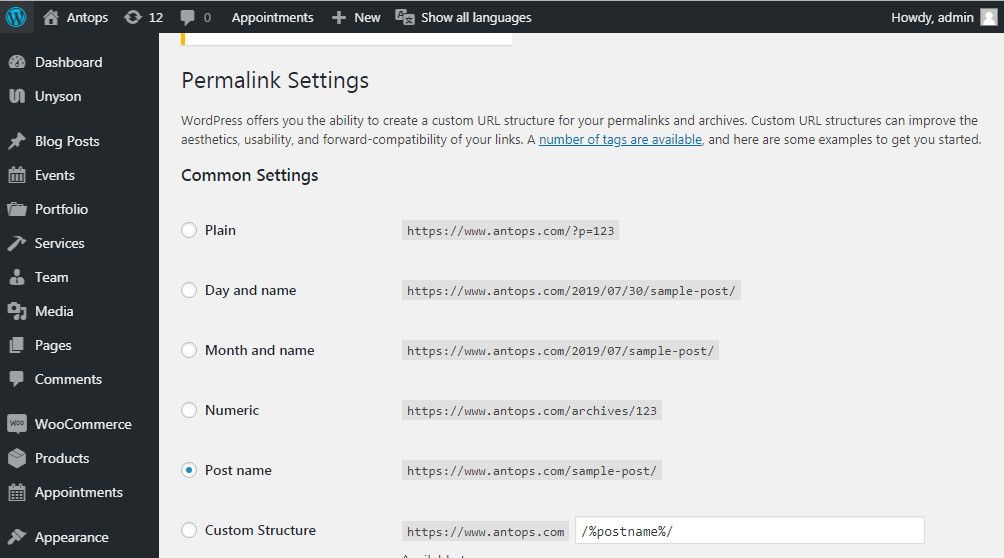
WordPress automatically facilitates the Plain permalink structure after you install WordPress. The number applied in the default permalink suggests WordPress where the content can be located in your database. To be more distinct, the number belongs to the ID of the table row in the wp_posts table of your WordPress database (the table prefix for your website will be changed if you changed it during the installation process). For example, https://www.antops.com/?p=123 would refer to the 123th row in your website’s wp_posts table.
The prefixed permalink structure is not user-friendly. It is better to introduce a visitor to a URL such as https://www.antops.com/sample-post than https://www.antops.com/?page_id=4651.
The part at the end of the permalink, i.e. ?p=123, is known as a query string. The question mark is a divider and the part that follows thereafter is the identifying data. In this case, we are identifying content from the database to present.
Google’s statement on the permalink of websites:
- URLs with a structured hierarchy will make it simpler for them to crawl your webpages.
- Visitors may skip off part of your URL when copying a link as the additional code might seem supplementary
- URLs that contain appropriate keywords will help you rank top in search engines
- Due to these reasons, it is better to use one a more search engine friendly permalink structure on your WordPress website.
Despite many people recommending differently, search engines such as Google can and do index URL’s that carry query strings. However, search engines do favor you to use “friendlier” URLs. And they’re placed higher ranks in results because of their semantic URL structure.
What is the Best WordPress Permalink Structure?
In general, most WordPress websites practice the following permalink arrangements:
- Post Name (
- Category and Name (
- Full Date and Name
( - Year, Month, and Name (
The post title and category and name permalink structures are also recommended because they do not specify the date an article was posted within the URL. If you publish evergreen content (or content that never goes out of date or is still be important for many years), you don’t need to use dates in your URL. However, many website owners take benefit of this and finally remove the publication date from all their items, which can be frustrating as a reader as you do not understand whether the information on the page is still solid.
Customizing the Category and Tag Base
At the foot of the permalink settings page, you will see optional settings for your category base and tag base. The default values for these fields are division and tag.
With the default settings, if you have a division on your website called WordPress, the URL of the WordPress section archives would be http://www.yourwebsite.com/category/wordpress/. Likewise, if you have a tag called Themes, the tag archive URL for that tag would be http://www.yourwebsite.com/tag/themes/.
Switching these fields allows you to replace the URLs that are used for archives. For example, you could change the category base to cat and the tag base to the topic. In our example, this would generate the archive URLs
http://www.yourwebsite.com/cat/wordpress/
and
http://www.yourwebsite.com/topic/themes/.
You should not keep your permalink default one. It decreases the chances of ranking up your page.