The magnets which do not lose their magnetic field are known as permanent magnets. The good permanent magnets have a high magnetic field and low mass. They are highly stable against demagnetizing influences. Magnetism is an important aspect of the electromagnetic force that is a fundamental force in the physical universe. A permanent magnet is also in the category of magnets, due to the orientation of its domains. These domains are the smaller magnetic fields, inherited in the crystalline structure, of the ferromagnetic materials. The ferromagnetic materials are only substances that are capable to be made into the magnets, and normally they are iron and nickel alloys.
A magnet can be created by following some conditions that cause the separation of domains in the ferromagnetic items and resultantly all are aligned to be in a similar direction. The permanent magnets can be created by heating of the ferromagnetic material to a certain level of high temperature. This temperature is specific for each kind of metal but it has the effect of fixing and aligning, the domains of the magnet in the permanent position. It is being said by the scientists, that there is the same process in the earth that causes the formation of permanent magnets.
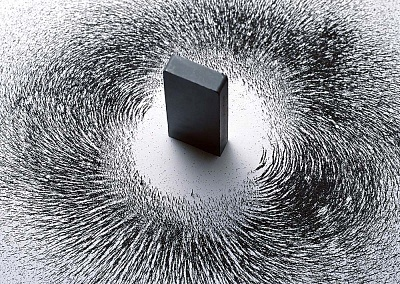
Steel as Permanent Magnet
The magnetization and demagnetization of steel are not easy. For its magnetization, a strong electric field is required. But once, if the steel is magnetized, then it can retain its magnetic properties. Due to this trait, the use of steel is highly recommended as a permanent magnet. But to ensure the structural stability, the steel is mixed with various other magnetic materials. But on the metallurgical basis, the alloys which are used for making the permanent magnets are very difficult to handle. Mechanically, these alloys are brittle and hard. After casting they can be ground to shape or even into powder. After converting to powder, they are mixed with the resin binders following by compressing and heat treating.
Uses of Permanent Magnets
Permanent magnets are significantly important due to their industrial applications, especially for electric motors and power generation. These magnets are used in galvanometers, magnetic door catches, compasses, generators, loudspeakers, and various other purposes. The induction process for generators and turbines also require permanent magnets for converting the mechanical motion to energy. These magnets are being used in the various electronics for the reverse induction of electric current to mechanical energy. Without using a permanent magnet, no one will be able to take advantage of electricity and modern-day appliances.