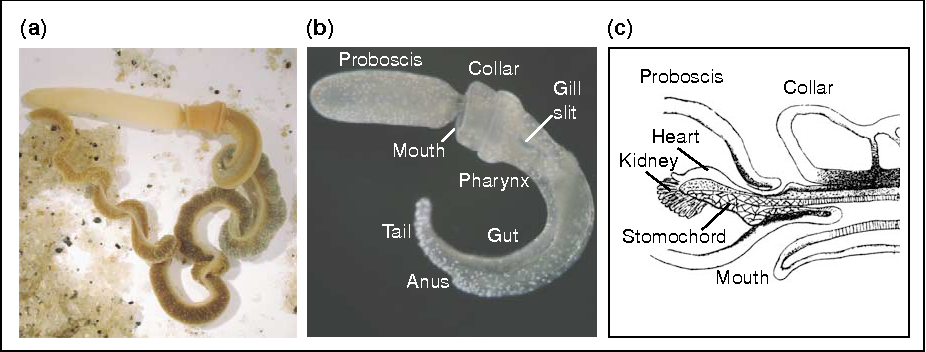
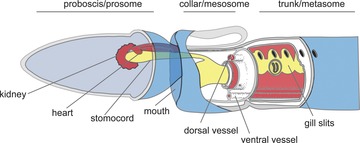
These animals have a rudimentary structure in the collar region called stomochord, which is a structure similar to the notochord and hence the name hemichordates.
Habitat: All members of this phylum are marine.
Examples:
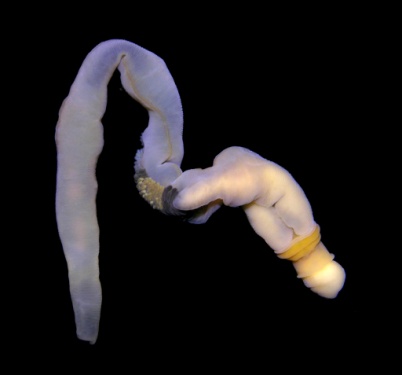

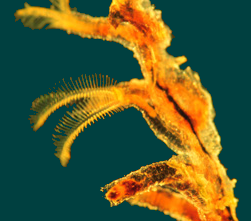
Balanoglossus Saccoglossus Rhabdopleura.
Body plan: They have organ-system level of organisation.
Symmetry: They are bilaterally symmetrical.
Germ layer: They are triploblastic and coelomate animals.
Body characteristics:
- Hemichordates have a worm-like body.
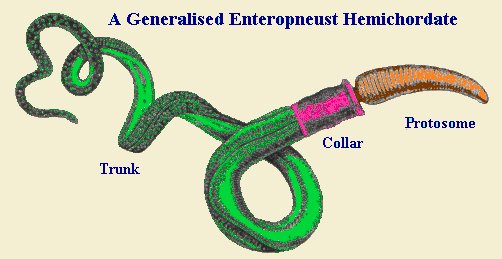
- The body is cylindrical and is divided into an anterior proboscis, a collar and a long trunk.
- There is a stomochord (or buccal diverticulum) in the collar region.
- They have pharyngeal gills similar to chordates.
- Both dorsal and ventral nerve cords are present in the body.
Physiology:
- Circulatory system is of open type.
- Respiration takes place through gills.
- Excretory organ is the proboscis gland.
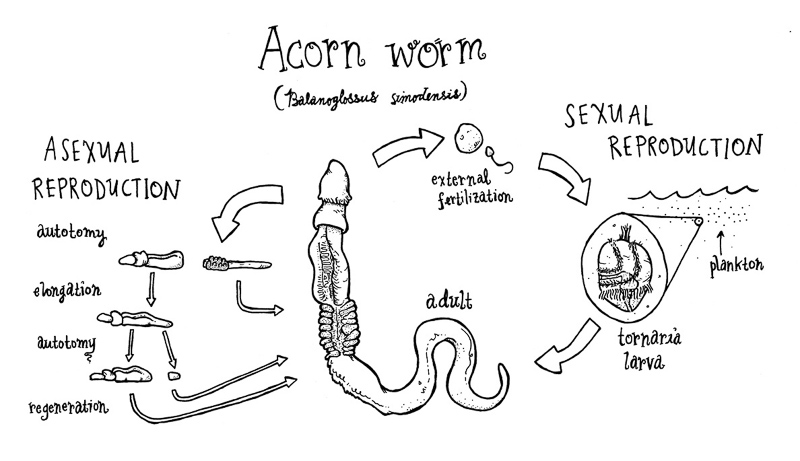
Reproduction: Sexes are separate (dioecious). Fertilisation is external.
Embryo Development: Development is indirect involving tornaria larva.