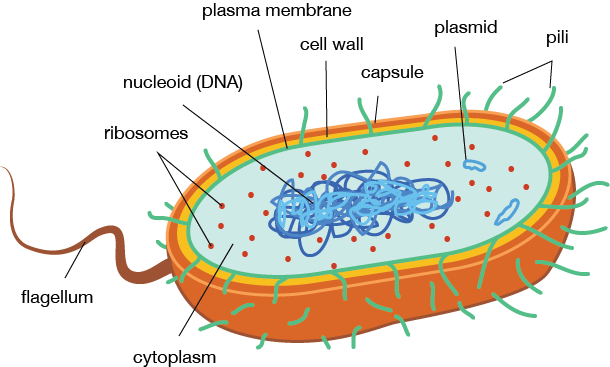
Cytoplasm
- The fluid matrix filling the cell is known as the cytoplasm.
- It is colloidal in nature and does not show streaming movement.
- It contains ribosomes, mesosomes, inclusion bodies, genetic material etc.
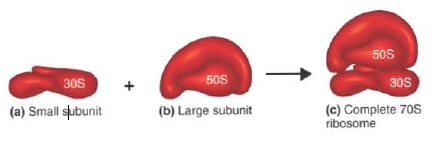
Ribosome
- In prokaryotes, ribosomes are found in association with the plasma membrane of the cell. It gives the cytoplasm a granular appearance.
- Ribosomes of prokaryotes are smaller than that of eukaryotic cells. They are about 15 nm by 20 nm in size.
- The prokaryotic ribosomes are of 70S type composed of two subunits – 30S and 50S subunits. But both have similar functions.
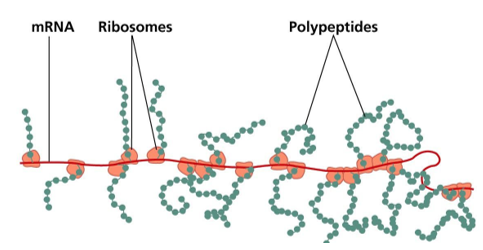
- Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
- Several ribosomes may attach to a single mRNA and form a chain called polyribosomes or polysome. The ribosomes of a polysome translate the mRNA into proteins.
Inclusions Bodies
- Reserve materials in prokaryotic cells are stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies.
- These are not bound by any membrane system and lie free in the cytoplasm.
- The inorganic inclusions are volutin granules and sulphur granules.
(Volutin granules are a storage form of phosphate)
- Gas vacuoles are found in photosynthetic bacteria (purple and blue green bacteria), cyanobacteria and a few aquatic forms. These are impermeable to water, but are permeable to atmospheric gases. These help the organism in floating.
- Storage granules: Nutrients and reserves may be stored in the cytoplasm in the form of glycogen (Glycogen granules), lipids, polyphosphate etc.
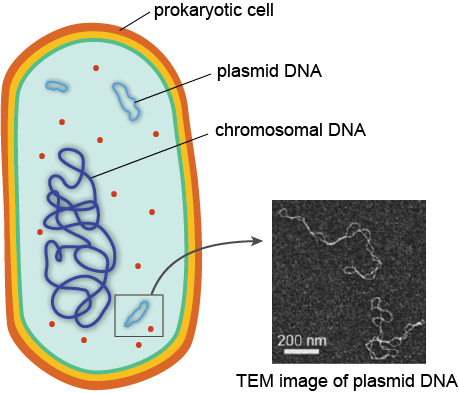
Nucleoid
- There is no well-defined nucleus.
- The genetic material is basically naked, not enveloped by a nuclear membrane.
- It is generally confined to the central region, and is termed as the nucleoid.
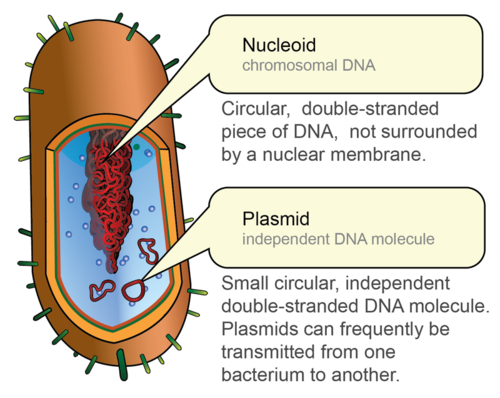
- In addition to the genomic DNA (the single chromosome/circular DNA), many bacteria have small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA.
- These smaller DNA are called plasmids.
- The plasmid DNA confers resistance to antibiotics to the organism.