Human beings regulate their respiration to suit the immediate needs of the body. The nervous system is responsible for respiration control by using special centers called the respiratory centers of the brain.
Respiratory centres of the brain
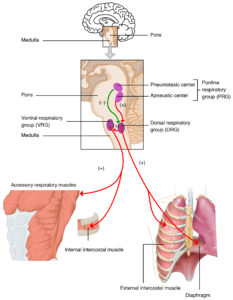
The neuronal signals passed between the respiratory centers of the brain and the diaphragm and muscles in the chest are used in the modulation of respiration. The three main centers of the brain used to regulate breathing are located in the medulla and pons parts of the brain. They can regulate respiration by the stimulation of the concentration of the intercostal muscles and diaphragm.
In medulla
Respiratory Rhythm Centre
Breathing takes place as an oscillating cycle where inspiration is followed by expiration; a cycle called the respiration rhythm. The respiration rhythm centre part of the brain is primarily responsible for regulating respiratory rhythms where it forms rhythmic nerve impulses that contract the muscles used for inhalation.
In normal cases, exhalation happens when muscles relax. In the case of rapid breathing, the respiratory centre is used to stimulate intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles for expiration.
In the pons
Pneumotaxic Centre
The actions of this centre are used in the prevention of lungs from over-inflation. The pneumotaxic centre controls the functions of the respiratory rhythm centre. The pneumataxic centre controls both the pattern and rate of breathing. It can send neural signals for the reduction of the duration of inspiration, thus affecting the rate at which respiration occurs.
It can also control the amount of air that the body inhales in a single breath. In the absence of this centre increases the breathing depth while decreasing the rate of respiration. This centre performs the opposite functions of the Apneustic centre as described below.
Apneustic Centre
The apneustic centre promotes inspiration by constant stimulation of the neurons located in the medulla region. It transmits signals that oppose the actions of the signals received from the pneumotaxic centre. The apneustic centre is used in the control of breathing intensity by sending positive signals to the neurons used in the regulation of inhalation.
Chemosensitive area
This area is located in the brain stem adjacent to the respiratory rhythm centre. It is an area highly sensitive to hydrogen and carbon dioxide ions. The area actsivated by the increase in carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions, which furthermore signals the rhythm centre for adjustment of the respiratory process to eliminate these substances.
In addition to the areas named earlier, there exist other receptors sensitive to changes in carbon dioxide and hydrogen concentration to send signals for breathing regulation. They are located in the medulla, carotid artery, aortic arch, bronchi and bronchioles.
Conclusion
Other factors that control the rate of respiration include temperature, water, light and carbon dioxide concentration.