Introduction
Genetic materials contribute to the fundamental role in the composition of living things. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is found in the nucleus of every cell and is precisely the same in each of them. The other genetic material that is found in cells and viruses is called ribonucleic acid (RNA).
DNA is the hereditary material found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells and in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that determines an organism’s composition. It is located in the nucleus of every cell, and it is exactly same in each of them. It stores so much information, thus requiring a high organization to keep all data safe for easy accessibility to the cell.
RNA is a polymer that is required in numerous biological roles in coding and decoding, regulation and expression of genes.
RNA and DNA are polymers composed of monomers known as nucleotides.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
In the nucleotides of ribonucleic acid, there exists a five-carbon sugar-phosphate linked to one of four acid bases: cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), and uracil (U).
. 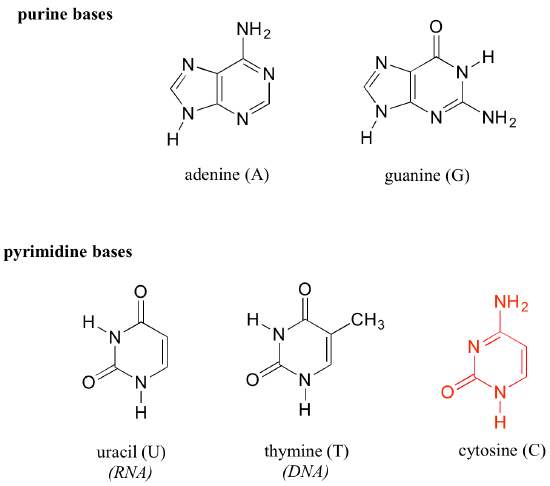
RNA is found in nature to be a single strand folded on itself, unlike the double-stranded DNA. Cellular living things use mRNA ( messenger ribonucleic acid) to convey genetic information. This employs the use of the nitrogenous bases of uracil, cytosine, adenine and guanine. On the other hand, viruses use the RNA genome to encode their genetic information. In protein synthesis, the process uses tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) molecules to deliver amino acids together in the formation of coded proteins.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
DNA is usually double-stranded whereby each strand is held together by the pairing of the nucleotides. These double strands of the deoxyribonucleic acid are spirally coiled to form a helix, hence sometimes known as a double helix. The DNA resembles a ladder where the nucleotides represent the rungs of the ladder while the phosphate and sugar are the sides of the ladder. The double helixes are furthermore wrapped around proteins known as histones and packaged into chromosomes.
In the nucleotide of a DNA, the sugar is missing the hydroxyl group at the position 2as illustrated in the figure below, and the thymine (T) is used in place of uracil (U). The prime symbol is used to differentiate the sugar carbon numbers from the numbers of the base carbon.
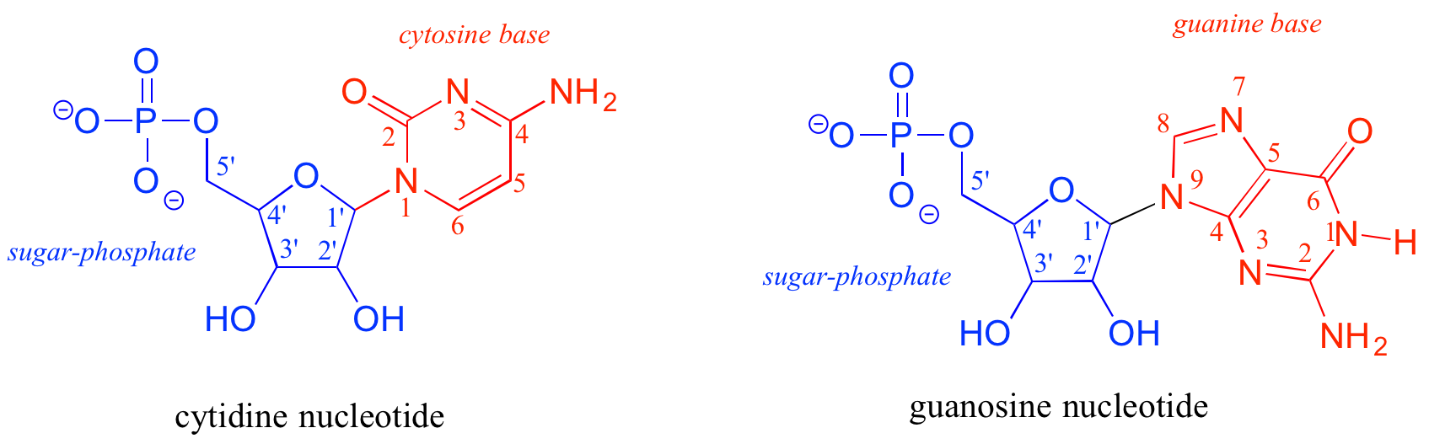
DNA exists in alternative forms such as A-DNA, B-DNA and Z-DNA. In functional organisms, A-DNA and B-DNA alone have been directly observed.