The java.lang.Throwable is the superclass of all exception classes in java.
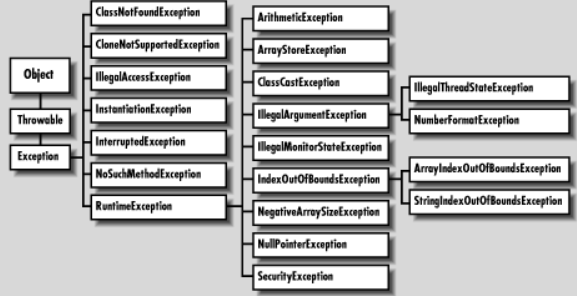
Hierarchy Exception
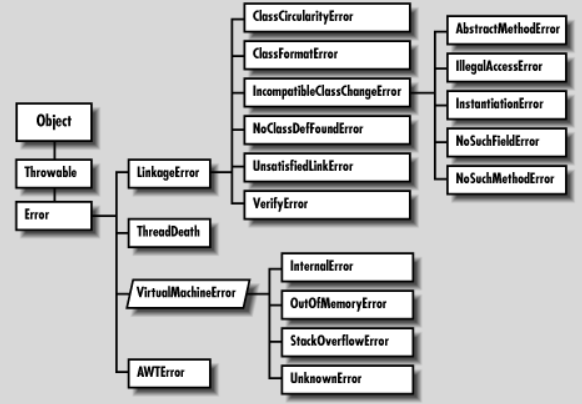
Hierarchy Error
Example
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int num1= 30, num2 = 0; // Try to divide by zero try { int result = num1 / num2; } catch (Throwable e) { System.out.println("Exceptionn class: " + e.getClass().getName()); e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
Output
Exceptionn class: java.lang.ArithmeticException java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at Main.main(Main.java:8) |
Java interview questions on Exception Handling
- what is an exception?
- How the exceptions are handled in java?
- What is the difference between error and exception in java?
- Can we keep other statements in between try catch and finally blocks?
- Explain the exception hierarchy in java?
- What are runtime exceptions in java?
- What is outofmemoryerror in java?
- What are checked and unchecked exceptions in java?
- What is the difference between classnotfoundexception and noclassdeffounderror in java?
- Will finally block get executed if return?
- Can we throw an exception without throws?
- What is rethrowing an exception in java?
- What is the use of throws keyword in java?
- What is exception propagation in java?
- Difference between throw and throws in java?
- What is finally in java?
- What is the difference between final finally and finalize in java?
- How to create customized exceptions in java?
- What is classcastexception in java?
- What is stackoverflowerror in java?
- What is the superclass of all exception classes?
- What is the use of printstacktrace method in java?
- What is arraystoreexception in java?