Thread life cycle:
- New.
- Runnable.
- Running.
- Blocked(Non-Runnable).
- Dead.
Diagram:
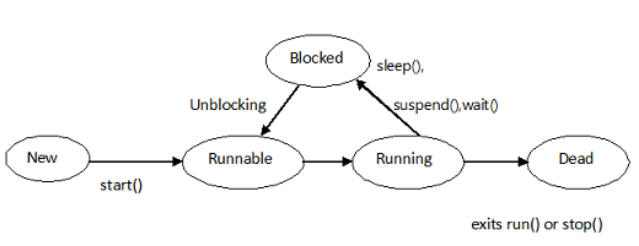
1. New: A new thread is created but not working. A thread after creation and before invocation of start() method will be in new state.
2. Runnable: A thread after invocation of start() method will be in runnable state. A thread in runnable state will be available for thread scheduler.
3. Running: A thread in execution after thread scheduler select it, it will be in running state.
4. Blocked: A thread which is alive but not in runnable or running state will be in blocked state. A thread can be in blocked state because of suspend(), sleep(), wait() methods or implicitly by JVM to perform I/O operations.
5. Dead: A thread after exiting from run() method will be in dead state. We can use stop() method to forcefully killed a thread.
Next Topic: Multithreading in java.
Previous Topic: Commonly used exception methods of Throwable class in java.