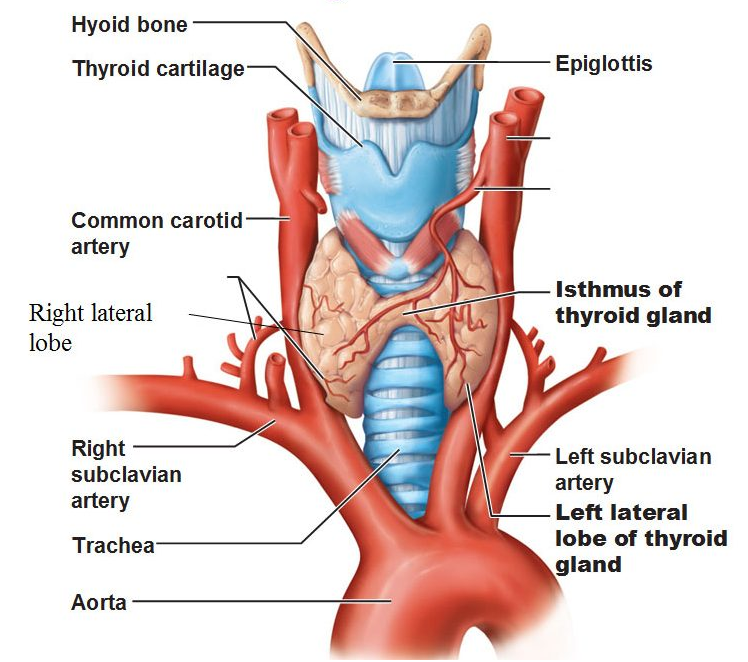
The thyroid gland is an essential part of the endocrine system and causes the production and release of thyroid hormones to the bloodstream. It is situated just below Adam’s apple at the front of the neck. Its shape is like a butterfly and it has two lobes which are located at either side of the trachea. Usually, a normal thyroid gland is not visible outwardly.
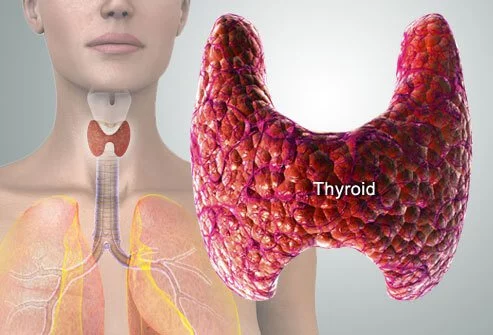
Functions of Thyroid Gland
The hormones produced by the thyroid gland are responsible for the regulation of metabolic rates of the body. Additionally, it is also involved in digestive functions, muscle control, heart and blood regulation, bone, and mood maintenance. The correct functioning of the thyroid gland is dependent on the good and adequate supply of iodine. The thyrotropin-releasing hormones control the release of thyroid hormones from the thyroid glands. For monitoring of the thyroid functioning of the patients, the free thyroid hormone, and thyroid-stimulating hormones are examined.
Hormones Produced by Thyroid Glands
The hormones produced by the thyroid glands are thyroxine, calcitonin. The thyroxine is a relatively inactive prohormone and the lower amounts of the active triiodothyronine hormone. Collectively these hormones are referred to as the thyroid hormones. Calcitonin is also produced from the C cells of the thyroid glands. It plays an important role in the regulation of calcium levels of the human body but its exact functioning in human beings is still unclear.
Disorders Associated with the Thyroid Gland
Sometimes, the thyroid glands can become overactive or underactive. Rarely it may occur from birth or can be later developed in life. The overactive thyroids cause a condition known as hyperthyroidism and cause the enlargement of the thyroid gland. Due to the overactivity of the thyroid gland, the level of hormones in the bloodstream is increased by many folds. The disorders of the thyroid glands may cause weight loss, irregular menstrual cycles, inflammation, intolerance to the heat, increased bowel movements, increased appetite, tiredness, tremor, irritability, hair loss, palpitations, and the retraction of the eyelids.
The low levels of the thyroid hormone result in hypothyroidism and this situation can result due to the use of certain drugs or by the low intake of iodine. The thyroid hormones are essential for mental and physical development, so hypothyroidism can result in reduced physical growth and learning difficulties. It causes the symptoms of intolerance to cold temperatures, weight gain, reduced appetite, depression, infertility, stiffness of muscles, and fatigue.